Centrifugal Force in Rotating Cylinder
(To be removed) Centrifugal force in rotating hydraulic cylinders
The Hydraulics (Isothermal) library will be removed in a future release. Use the Isothermal Liquid library instead.
For more information on updating your models, see Upgrading Hydraulic Models to Use Isothermal Liquid Blocks.
Library
Hydraulic Cylinders
Description
The Centrifugal Force in Rotating Cylinder block is a building block to be used in hydraulic cylinder models, to account for centrifugal forces exerted by fluid on a piston, if the cylinder rotates about its symmetry axis. Such cylinders are used in control mechanisms of various friction clutches, brakes, square-jaw positive clutches, dog clutches, and so on. No inertial effects are considered in the model. In other words, the angular velocity is assumed to be constant or changing at very low speed.
The centrifugal force is computed with the following equation:
where
| F | Centrifugal force |
| ro | Piston outer radius |
| ri | Piston inner radius |
| rp | Fluid entry radius. For design purposes, |
| ρ | Fluid density |
| ω | Shaft angular velocity |
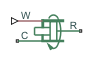
Connections R and C are mechanical translational conserving ports corresponding to the cylinder rod and case, respectively. Connection W is a physical signal port through which shaft angular velocity is imported. The block directionality is adjustable and can be controlled with the Cylinder orientation parameter.
Basic Assumptions and Limitations
No inertial effects are considered in the model; that is, the angular velocity of the cylinder is assumed to be constant or changing at very low speed.
Fluid inertia is not taken into account.
Fluid compressibility is not taken into account.
Parameters
- Piston outer radius
The default value is
0.1m.- Piston inner radius
The default value is
0.05m.- Fluid entry radius
The default value is
0.06m.- Fluid density
The default value is
880kg/m^3.- Cylinder orientation
Specifies block orientation with respect to the globally assigned positive direction. The block can be installed in two different ways, depending upon whether it exerts force in the positive or in the negative direction. If positive velocity applied at port W exerts force in negative direction, set the parameter to
Acts in negative direction. The default value isActs in positive direction.
Examples
The following schematic diagram shows a model of a custom single-acting hydraulic cylinder built of the Single-Acting Hydraulic Cylinder, Rotating Pipe, and Centrifugal Force in Rotating Cylinder blocks.

The centrifugal force generated by the Centrifugal Force in Rotating Cylinder block sums up with that of the cylinder at node A. The Rotating Pipe block simulates the pipeline between the cylinder chamber and the channel in the center of a rotating shaft where the cylinder is installed.
Ports
The block has the following ports:
RMechanical translational conserving port associated with the cylinder rod.
CMechanical translational conserving port associated with the cylinder clamping structure.
WPhysical signal port providing the angular velocity value.