demdataui
(Removed) UI for selecting digital elevation data
The demdataui function has been removed. Use the readgeoraster function instead.
Syntax
Description
demdataui is a graphical user interface to extract digital
elevation map data from a number of external data files. You can extract data to
MAT-files or the base workspace as regular data grids with referencing
vectors.
The demdataui panel lets you read data from a variety of
high-resolution digital elevation maps (DEMs). These DEMs range in resolution from
about 10 kilometers to 100 meters or less. The data files are available over the
Internet at no cost, or (in some cases) on CD-ROMs for varying fees.
demdataui reads ETOPO5, TerrainBase, GTOPO30, GLOBE,
satellite bathymetry from Smith and Sandwell, and DTED data.
demdataui looks for these geospatial data files on the
MATLAB® path and, for some operating systems, on CD-ROM disks.
Note
When it opens, demdataui scans your Mapping Toolbox™ path for candidate data files. On PCs, it also checks the root
directories of CD-ROMs and other drives, including mapped network drives.
This can cause a delay before the GUI appears.
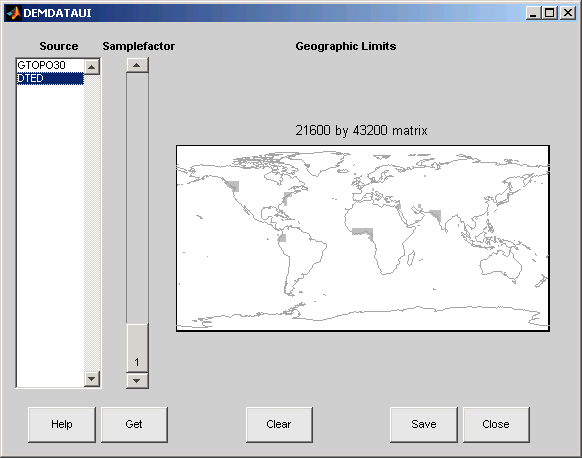
You use the list to select the source of data and the map to select the region of interest. When you click the Get button, data is extracted and displayed on the map. Use the Save button to save the data in a MAT-file or to the base workspace for later display. The Close button closes the window.
Controls

The Map
The map controls the geographic extent of the data to be extracted.
demdataui extracts data for areas currently visible on the
map. Use the mouse to zoom in or out to the area of interest. See zoom for more on zooming.
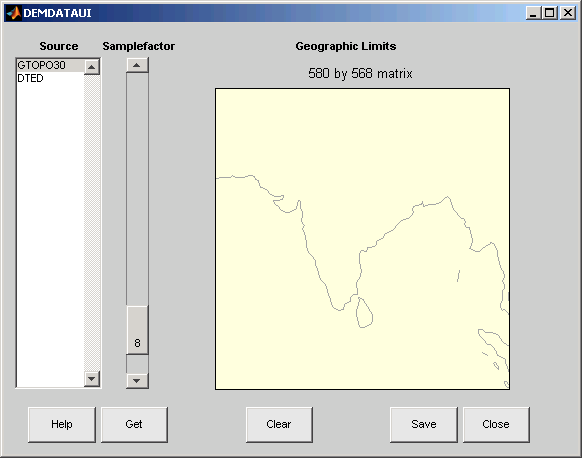
Some data sources divide the world up into tiles. When extracting, data is concatenated across all visible tiles. The map shows the tiles in light yellow with light gray edges. When data resolution is high, extracting data for large area can take much time and memory. An approximate count of the number of points is shown above the map. Use the Samplefactor slider to reduce the amount of data.
The List
The list controls the source of data to be extracted. Click a name to see the
geographic coverage in light yellow. The sources list shows the data sources found
when demdataui started.
demdataui searches for data files on the MATLAB path. On some computers, demdataui also checks
for data files on the root level of letter drives. demdataui
looks for the following data:
etopo5: The filesnew_etopo5.biloretopo5.northern.batandetopo5.southern.bat.tbase: The filetbase.bin.satbath: The filetopo_6.2.img.gtopo30: A folder that contains subfolders with the data files. For example,demdatauiwould detect GTOPO30 data if a folder on the path contained the folders E060S10 and E100S10, each of which holds the uncompressed data files.globedem: A folder that contains data files and in the subfolder/esri/hdrand the*.hdrheader files.dted: A folder that has a subfolder named DTED. The contents of the DTED folder are more subfolders organized by longitude and, below that, the DTED data files for each latitude tile.
The Samplefactor Slider
The Sample Factor slider allows you to reduce the density of the data. A sample factor of 2 returns every second point. The current sample factor is shown on the slider.
The Get Button
The Get button reads the currently selected data and displays it on the map. Press the standard interrupt key combination for your platform to interrupt the process.
The Clear Button
The Clear button removes any previously read data from the map.
The Save Button
The Save button saves the currently displayed data to a
MAT-file or the base workspace. If you choose to save to a file, you will be
prompted for a file name and location. If you choose to save to the base workspace,
you can choose the variable name under which the data will be stored. The
demdataui function returns one or more matrices as an array
of display structures, having one element for each separate
get you requested (assuming you did not subsequently
Clear).
Data are returned as Mapping Toolbox Version 1 display structures. For information about display structure
format, see Version 1 Display Structures in the
reference page for displaym.
Use load and displaym to redisplay the
data from a file on an axesm-based map. To display the data in
the base workspace, use displaym. To gain access to the data
matrices, subscript into the structure (for example, datagrid =
demdata(1).map; refvec = demdata(1).maplegend. Use
worldmap to create easy displays of the elevation data (for
example, worldmap(datagrid,refvec). Use
meshm to add regular data grids to existing displays, or
surfm or a similar function for geolocated data grids (for
example, meshm(datagrid,refvec) or
surfm(latgrat,longrat,z).
The Close Button
The Close button closes the demdataui
panel.
Examples
Tips
If
demdatauidoes not recognize data you think it should find, check your path and click Help to read about how files are identified.You can add the data grids to an
axesm-based map by using thegeoshowfunction.Updating the data returned by
demdatauito geographic data structures (geostructs) using theupdategeostructfunction is not supported because they are of typesurface.