Generic target options
Specify size of data types and endianness by creating your own target processor
Description
If a target processor is not directly supported by Polyspace®, you can create your own target. You specify the target
mcpu representing a generic "Micro Controller/Processor
Unit" and then explicitly specify sizes of fundamental data types, endianness and other
characteristics.
Settings
In the user interface of the Polyspace desktop products, the Generic target options dialog
box opens when you set the Target processor type to
mcpu. The Target processor type
option is available on the Target & Compiler node in the
Configuration pane.
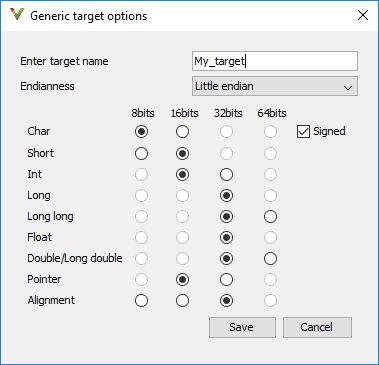
Use the dialog box to specify the name of a new mcpu
target, for example My_target. That new target is added to the
Target processor type option list.
Default characteristics of a new target: listed as
type
[size]
char
[8]short
[16]int
[16]long
[32]long long
[32]float
[32]double
[32]long double
[32]pointer
[16]alignment
[32]char is signed
endianness is little-endian
Command-Line Options
When using the command line, use -target mcpu along with
these target specification options.
| Option | Description | Available With | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
-little-endian | Little-endian architectures are Less Significant byte First (LSF). For example: i386. Specifies that the less significant byte of a short integer (e.g. 0x00FF) is stored at the first byte (0xFF) and the most significant byte (0x00) at the second byte. | All targets | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-little-endian |
-big-endian | Big-endian architectures are Most Significant byte First (MSF). For example: SPARC, m68k. Specifies that the most significant byte of a short integer (e.g. 0x00FF) is stored at the first byte (0x00) and the less significant byte (0xFF) at the second byte. | All targets | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-big-endian |
-default-sign-of-char [signed | unsigned] | Specify default sign of
| All targets | polyspace-bug-finder -default-sign-of-char unsigned -target
mcpu |
-char-is-16bits |
Incompatible
with | mcpu | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-char-is-16bits |
-short-is-8bits | Define short as 8 bits, regardless of sign | mcpu | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-short-is-8bits |
-int-is-32bits | Define int as 32 bits, regardless of sign.
Alignment is also set to 32 bits. | mcpu, hc08, hc12, mpc5xx | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-int-is-32bits |
-long-is-32bits | Define If your project
sets | All targets | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-long-is-32bits |
-long-long-is-64bits | Define long long as 64 bits, regardless
of sign. Alignment is also set to 64 bits. | mcpu | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-long-long-is-64bits |
-double-is-64bits | Define double and long double as
64 bits, regardless of sign. | mcpu, sharc21x61, hc08, hc12, mpc5xx | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-double-is-64bits |
-pointer-is-24bits | Define pointer as 24 bits, regardless of sign. | c18 | polyspace-bug-finder -target c18
-pointer-is-24bits |
-pointer-is-32bits | Define pointer as 32 bits, regardless of sign. | mcpu | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu
-pointer-is-32bits |
-align [128|64|32|16|8] | Specifies the largest alignment of scalar objects, structures, classes, unions, or arrays to the 128, 64, 32, 16, or 8 bit boundaries. For instance, if the alignment of basic types in an array or struct is always 8, the array or struct storage is strictly determined by the size of the individual data objects without member and end padding. | All targets | polyspace-bug-finder -target mcpu -align
16 |
See also:
You can also use the option -custom-target
to specify sizes in bytes of fundamental data types, signedness of plain
char, alignment of structures and underlying types of standard
typedef-s such as size_t,
wchar_t and ptrdiff_t.
Examples
GCC Toolchains
If you use any of these GCC toolchains for your software development, you can setup your Polyspace analysis so that your code compiles with Polyspace:
ARM® Ltd. GNU® Arm Embedded Toolchain
HighTec EDV-Systeme
Linaro® GNU cross-toolchain
Melexis®
MENTOR® Embedded Sourcery™ CodeBench
QNX® Software Development Platform
Rowley Associates' CrossWorks
STMicroelectronics® TrueSTUDIO® for STM32
Texas Instruments® Code Composer Studio™
Wind River® GNU Compiler
Use polyspace-configure on a build command that
uses one of these toolchains and extract information about your
compiler configuration. The command creates a Polyspace project by default. To generate an options file
that you then pass to Polyspace at the command line, run
polyspace-configure with the option
-output-options-file.
Alternatively, to manually set the details of your compiler configuration at the command line:
Select the
gnu#.xcompiler that corresponds to your compiler version by using theCompiler (-compiler)option.Specify your target by using the Command-Line Options. For an example of targets you can specify, see Targets for GCC and Clang Based Compilers.
Specify your compiler macro definitions by using the
Preprocessor definitions (-D)option.
Targets for GCC and Clang Based Compilers
If you select one of the gnu#.x or
clang#.x compilers with the option
Compiler (-compiler),
you can specify one of the supported target processor types. See
Target processor type
(-target). If a target processor type is not
directly listed as supported, you can create the target by using
the generic target options.
These tables show examples of targets that you can create:
GCC Based Compiler Targets
| Target | Options |
|---|---|
| ARM |
|
| ARM64 |
|
| MSP430 |
|
| RISC-V | Here:
|
| PowerPC |
|
| Tricore |
|
Clang Based Compiler Targets
| Target | Options |
|---|---|
| Cadence Tensilica Xtensa |
|
Emulate Microchip MPLAB XC16 and XC32 Compilers
If you build your source code using Microchip MPLAB XC16 or XC32 compilers, you can set up your Polyspace analysis so that your code compiles with Polyspace. Enter these options at the command line or specify them in the Configuration pane of the Polyspace desktop user interface.
| Compiler | Target Processor Families | Options |
|---|---|---|
| MPLAB XC16 | PIC24 dsPIC |
|
| MPLAB XC32 | PIC32 |
|
The set of macros specified with the option
Preprocessor definitions
(-D) is a minimal set. Specify additional
macros as needed to ensure your code compiles with
Polyspace.
Tips
If you use Polyspace as You Code extensions in IDEs, enter this option in an analysis options file. See options file.