imblend
Description
I = imblend(___,Name=Value)Mode="Guided" specifies to use the guided mode for image
blending.
Examples
Load an image into the workspace as the background image.
bg = imread("cameraman.tif");
figure
imshow(bg)
Create a foreground image of a digital object to blend, as augmented reality, with the cameraman scene.
fg = imread("coins.png");
figure
imshow(fg)
To blend only one coin in the image, create a mask by segmenting one coin in the foreground image.
[centers,radii] = imfindcircles(fg,[15 30]); centers = centers(1,:); radii = radii(1,:); mask = circles2mask(centers,radii,size(fg)); figure imshow(mask)

Blend the foreground image with the background image using alpha blending. Visualize the blended image.
I = imblend(fg,bg,mask,Location=[-10 40]); figure imshow(I)
Load an image into the workspace as the background image.
bg = imread("peppers.png");
figure
imshow(bg)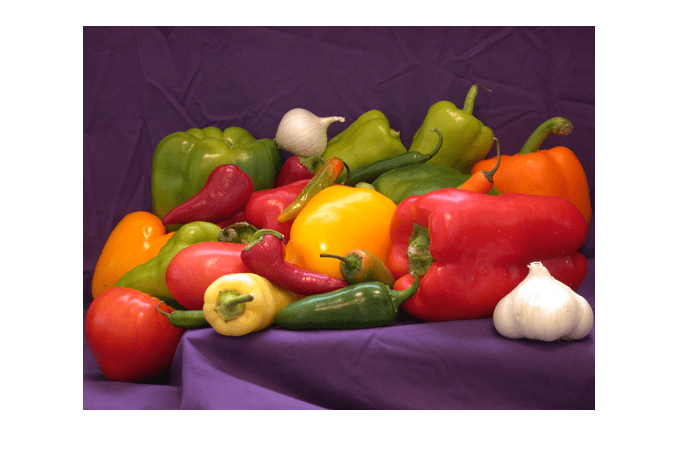
Load a foreground image of an object to blend with the background image.
fg = imread("strawberries.jpg");
fg = fg(510:end,1:390,:);
fg = imresize(fg,0.5);
figure
imshow(fg)
Create a mask for blending the entire foreground image with a section of the background image.
mask = true(size(fg,1),size(fg,2));
Blend the foreground image with the background image at the location specified by the mask using different blend modes. Visualize and compare the blended images from the different blend modes.
Mode
Alphacreates a partial transparency effect.Mode
Guidedchanges the transition region between the foreground and background images.Mode
Poissonblends the foreground image seamlessly with the background image, but obscures some details of the background image.Mode
PoissonMixGradientsblends the foreground image seamlessly with the background image without obscuring details of the background image.Mode
Minretains the darkest areas in the foreground and background images.Mode
Maxretains the brightest areas in the foreground and background images.Mode
Averageaverages the foreground and background images.Mode
Overlayretains the highlights and shadows of the background image while integrating the textures of the foreground image.
I1 = imblend(fg,bg,Mode="Alpha",Location=[270 270],ForegroundOpacity=0.6); I2 = imblend(fg,bg,mask,Mode="Guided",Location=[270 270],FilterSize=[5 5]); I3 = imblend(fg,bg,mask,Mode="Poisson",Location=[270 270]); I4 = imblend(fg,bg,mask,Mode="PoissonMixGradients",Location=[270 270]); I5 = imblend(fg,bg,Mode="Min",Location=[270 270]); I6 = imblend(fg,bg,Mode="Max",Location=[270 270]); I7 = imblend(fg,bg,Mode="Average",Location=[270 270]); I8 = imblend(fg,bg,Mode="Overlay",Location=[270 270]); figure(Position=[0 0 1000 1000]) tiledlayout(4,2) nexttile imshow(I1) title("Mode = Alpha") nexttile imshow(I2) title("Mode = Guided") nexttile imshow(I3) title("Mode = Poisson") nexttile imshow(I4) title("Mode = PoissonMixGradients") nexttile imshow(I5) title("Mode = Min") nexttile imshow(I6) title("Mode = Max") nexttile imshow(I7) title("Mode = Average") nexttile imshow(I8) title("Mode = Overlay")

Input Arguments
Foreground image, specified as a 2-D grayscale image or 2-D RGB image. The size of the foreground image can be different from the size of the background image. The function uses the first minRows rows and the first minCols columns of the foreground image for blending, where minRows is the minimum of the number of rows between the foreground and background images, and minCols is the minimum of the number of columns between the foreground and background images.
Data Types: single | double | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Background image, specified as a 2-D grayscale image or 2-D RGB image.
Data Types: single | double | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Mask of foreground pixels to blend, specified as a numeric or
logical 1 (true) or 0
(false), or a numeric or logical matrix of the same size as the foreground image.
For numeric input,
any nonzero pixels are considered to be 1 (true). If mask is a scalar with a value of
true, all pixels of the foreground image are included in the
mask.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: imblend(F,B,Location=[10 12]) specifies that the blending of
the foreground image must start from the 10th row and 12th column of the background
image.
Blend mode, specified as "Alpha", "Guided",
"Poisson", "PoissonMixGradients",
"Min", "Max", "Average", or
"Overlay". When the blend mode is "Poisson" or
"PoissonMixGradients", you must specify the mask
argument.
| Blend Mode | Algorithm | Output | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
"Alpha" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as augmented reality, computer-generated graphics, and multimodal medical image visualization. |
"Guided" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as augmented reality and computer-generated graphics. |
"Poisson" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as photo editing, panorama stitching of multiple photos, or augmented reality applications such as virtually trying on clothes. |
"PoissonMixGradients" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as photo editing, panorama stitching of multiple photos, or augmented reality applications such as virtually trying on clothes. |
"Min" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as astrophotography, for noise reduction, or in security applications to enhance details in dark regions. |
"Max" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as medical imaging to emphasize certain features, or in surveillance to detect motion or changes in a series of images. |
"Average" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as noise reduction in photography, where averaging multiple shots of the same scene can reduce random noise. |
"Overlay" |
|
| You can use this mode in applications such as digital art and photo editing to add textures, adjust lighting, or create special effects by blending textures or patterns with original photographs. |
Data Types: char | string
Starting location of blending in the background image, specified as a 1-by-2 numeric vector. The first and second elements specify the x-coordinate (column index) and y-coordinate (row index), respectively, of the location in the background image from where the top-left corner of the foreground image is blended. The row and column indices of the starting location can be zero, negative, or even fractional. The function determines the mapping between the pixels of the background and foreground images for blending by using image translation and interpolation.
Data Types: single | double
Opacity of the foreground in alpha blending, specified as a positive scalar less than or equal to 1. Decreasing the foreground opacity increases the partial transparency effect in the blended image.
Note
Specify ForegroundOpacity only when
Mode is "Alpha".
Data Types: single | double
Size of the filter in guided blending, specified as a 2-element vector of positive integers. Increasing the filter size increases the smoothing of the edges of the mask.
Note
Specify FilterSize only when Mode is
"Guided".
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Output Arguments
Blended image, returned as a 2-D grayscale or RGB image with the same size and data type as the background image.
References
[1] Di Martino, J. Matías, Gabriele Facciolo, and Enric Meinhardt-Llopis. “Poisson Image Editing.” Image Processing On Line 6 (November 18, 2016): 300–325. https://doi.org/10.5201/ipol.2016.163.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
imblendsupports the generation of C and C++ code (requires MATLAB® Coder™). For more information, see Code Generation for Image Processing.Name-value arguments must be compile-time constants.
Version History
Introduced in R2024bBlend images seamlessly using the Poisson blend modes. "Poisson"
preserves the gradient of the foreground image, while
"PoissonMixGradients" mixes the gradients of foreground and background
images.
imblend now supports the generation of
C code (requires MATLAB
Coder).
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)







