Communications
Use these examples to learn how to model different types of data transmission.
Featured Examples
AM Radio Receiver
A simplified AM radio receiver. A single tone signal at 2kHz is transmitted with a carrier frequency of 600kHz. The variable capacitor, Cres, in the resonant circuit is used in order to sweep through a certain frequency span. When the resonance passes through 600kHz, the signal is picked up and amplified by a two-stage Class A RF power amplifier. The signal is finally extracted by a diode detector, where it would normally be passed on to an audio amplifier (not included here). The Scope displays the final output, the value of the resonant capacitance, and the received and amplified signals.
ARINC 429 Communication Link
A communication link that follows the ARINC 429 specification. Here it is configured for 100kBits per second operation. The ARINC 429 specification is for a simplex broadcast bus with odd parity checking. The cable is a balanced line comprising a twisted pair for data wires A and B, plus an outer shield. This model can be used to check compliance with the ARINC 429 specification, and to assess the impact of different cable lengths, cable parameters and abstracted transmitter and receiver characteristics. It can also be used to check operation with multiple receivers, the ARINC 429 specification allowing for up to 20 receivers to connect to a single transmitter.
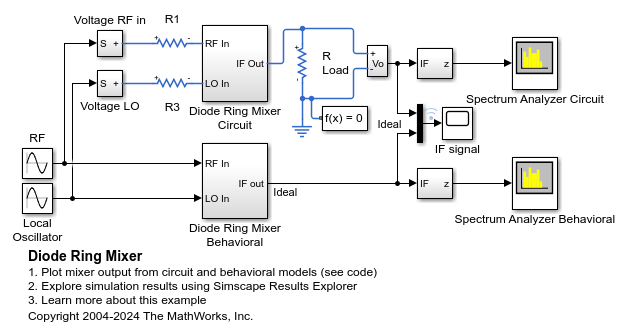
Diode Ring Mixer
How a diode ring can be used to demodulate a frequency-modulated signal. The RF input has a fixed frequency of 9MHz, and the local oscillator has a fixed frequency of 11MHz. Hence the frequency-modulated signal is a sine wave of 2MHz. This 2MHz component is clearly visible in the IF response. The second component in the IF response is the sum of the RF and local oscillator frequencies i.e. 20MHz.
LC Transmission Line and Test Bridge
A transmission line model and bi-directional test bridge. Reflected and transmitted signals are slightly different if the test direction is changed. This is because the line model is not symmetric. This type of model can be used both to explore the impact of cable choice on transmission characteristics, and also to compare relative fidelity of different transmission line model structures and parameterizations.
Multiplier Integrated Circuit
How the Multiplier block can be used to multiply or divide two input voltages. In both cases, slew rate limiting occurs until the final voltage is reached. Note that the input-side circuits must have an Electrical Reference block so that the solver can determine a voltage for every node.
Phase-Locked Loop
How to model a phase-locked loop. The charge pump and filter are modeled using discrete analog components whereas the oscillator is represented as behavioral component using the Simscape™ Electrical™ Voltage-Controlled Oscillator block. The D-type flip-flops in the phase detector are represented in a simplified form using Simulink® blocks to define the behavior, and electrical components are used just at the interface. Non-zero initial conditions are applied to C1 and C2 in order to start the VCO out of phase and test the tracking ability.
Simulate Backplane Channel in Simscape Using S-Parameters
Simulate a differential high-speed backplane channel in Simscape™ using the S-Parameter Rational Fit block. You compare the output of a simulated electrical model for different values of the Rational fit object parameter.
- Since R2025a
- Open Live Script
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)