Write Applications for macOS
Objective-C/C++ Applications for Apple Cocoa API
Apple Xcode, implemented in the Objective-C language, is used to develop applications using the Cocoa framework, the native object-oriented API for the macOS operating system.
This article details how to create a graphical MATLAB® application with Objective C and Cocoa, and then deploy it using MATLAB Compiler SDK™.
Where Is the Example Code?
You can find example Apple Xcode, header, and project files in
matlabroot/extern/examples/compilersdk/c_cpp/triangle/xcode
Preparing Your Apple Xcode Development Environment
To run this example, you should have prior experience with the Apple Xcode development environment and the Cocoa framework.
The example in this article is ready to build and run. However, before you build and run your own applications, you must do the following (as has been done in our example code):
Build the shared library with MATLAB Compiler SDK using either Library Compiler,
compiler.build.cppSharedLibrary, ormcc.Compile application code against the library’s header file and link the application against the component library and
libmwmclmcrrt.In your Apple Xcode project:
Specify
mccin the project target (Build Component Library in the example code).Specify target settings in
HEADER_SEARCH_PATHS.Specify directories containing the library header.
Specify the path
matlabroot/extern/includeDefine
MWINSTALL_ROOT, which establishes the install route using a relative path.
Set
LIBRARY_SEARCH_PATHSto any directories containing the shared library, as well as to the pathmatlabroot/runtime/maci64matlabroot/runtime/maca64
Build and Run the Sierpinski Application
In this example, deploy the graphical Sierpinski function
sierpinski.m, located at
matlabroot/extern/examples/compilersdk/c_cpp/triangle
function [x, y] = sierpinski(iterations, draw) % SIERPINSKI Calculate (optionally draw) the points % in Sierpinski's triangle % Copyright 2004 The MathWorks, Inc. % Three points defining a nice wide triangle points = [0.5 0.9 ; 0.1 0.1 ; 0.9 0.1]; % Select an initial point current = rand(1, 2); % Create a figure window if (draw == true) f = figure; hold on; end % Pre-allocate space for the results, to improve performance x = zeros(1,iterations); y = zeros(1,iterations); % Iterate for i = 1:iterations % Select point at random index = floor(rand * 3) + 1; % Calculate midpoint between current point and random point current(1) = (current(1) + points(index, 1)) / 2; current(2) = (current(2) + points(index, 2)) / 2; % Plot that point if draw, line(current(1),current(2));, end x(i) = current(1); y(i) = current(2); end if (draw) drawnow; end
Using the Mac Finder, locate the Apple Xcode project (
matlabroot/extern/examples/compilersdk/c_cpp/triangle/xcodeOpen
sierpinski.xcodeproj. The development environment starts.In the Groups and Files pane, select Targets.
Click Build and Run. The make file runs that launches MATLAB Compiler™ (
mcc).
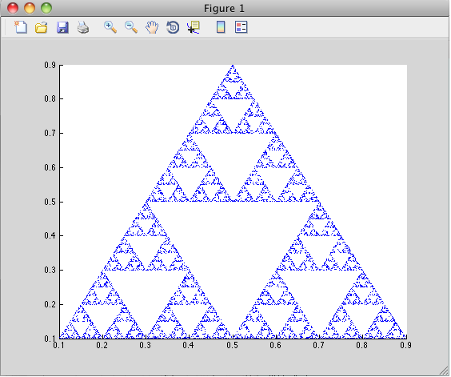
Running the Sierpinski Application
Run the Sierpinski application from the build output directory. The following GUI appears:
MATLAB Sierpinski Function Implemented in the Mac Cocoa Environment
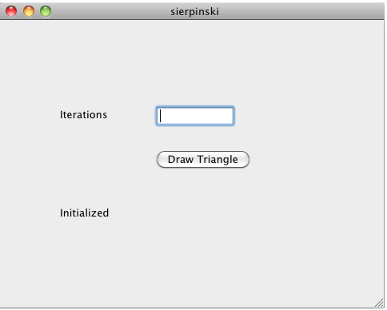
In the Iterations field, enter an integer such as
10000: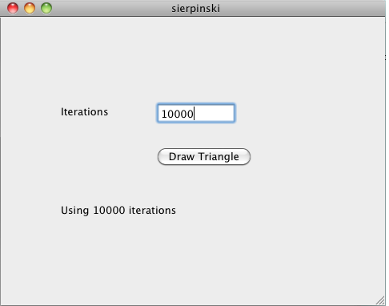
Click Draw Triangle. The following figure appears: