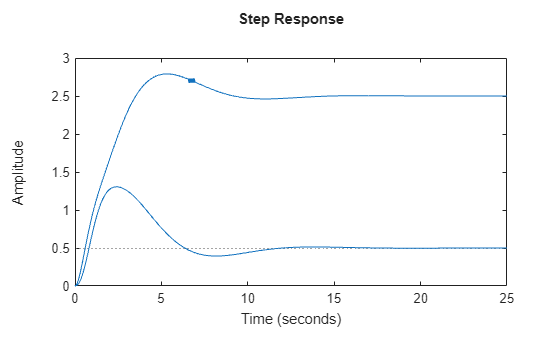
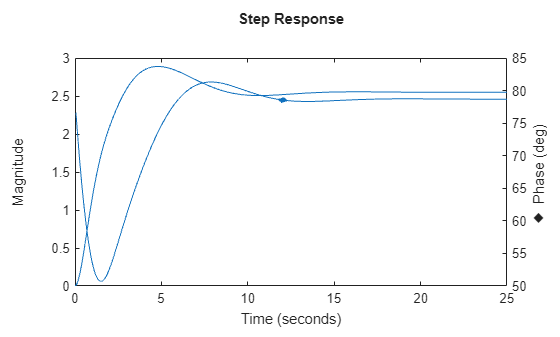
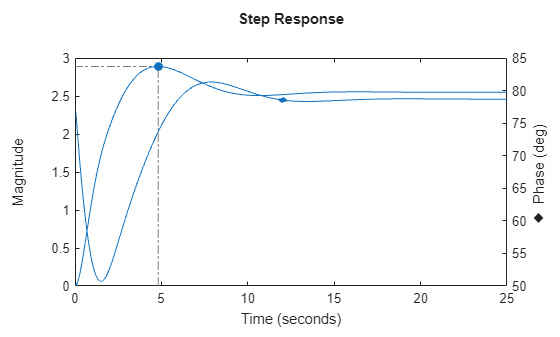
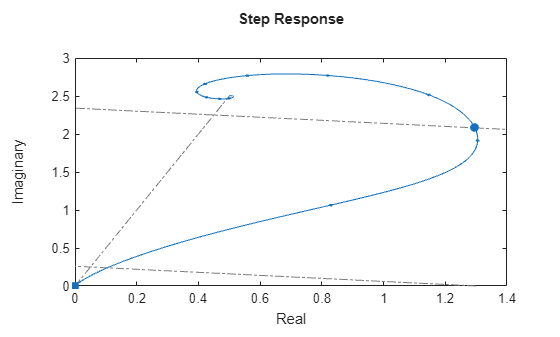
stepplot
Plot step response of dynamic system
Description
The stepplot function plots the step response of a dynamic system model and returns a
StepPlot chart object. To customize the plot, modify the properties of the
chart object using dot notation. For more information, see Customize Linear Analysis Plots at Command Line (Control System Toolbox).
To obtain step response data, use the step function.
Creation
Syntax
Description
sp = stepplot(sys)sys and returns
the corresponding chart object.
If sys is a multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) model, then the
stepplot function creates a grid of plots with each plot displaying
the step response of one input-output pair.
If sys is a model with
complex coefficients, then the plot shows both the real and imaginary components of the
response on a single axes and indicates the imaginary component with a diamond marker.
You can also view the response using magnitude-phase and complex-plane plots. (since R2025a)
sp = stepplot(___,t)t. You can
use t with any of the input argument combinations in previous
syntaxes. To define the time steps, you can specify:
The final simulation time using a scalar value
The initial and final simulation times using a two-element vector (since R2023b)
All the time steps using a vector
sp = stepplot(___,config)RespConfig to create config.
sp = stepplot(___,plotoptions)plotoptions. Settings you specify in
plotoptions override the plotting preferences for the current
MATLAB® session. This syntax is useful when you want to write a script to generate
multiple plots that look the same regardless of the local preferences.
sp = stepplot(parent,___)Figure or TiledChartLayout, and sets the
Parent property. Use this syntax when you want to create a plot
in a specified open figure or when creating apps in App Designer.
Input Arguments
Properties
Object Functions
addResponse | Add dynamic system response to existing response plot |
showConfidence | Display confidence regions on response plots for identified models |
Examples
Tips
Plots created using
stepplotdo not support multiline titles or labels specified as string arrays or cell arrays of character vectors. To specify multiline titles and labels, use a single string with anewlinecharacter.stepplot(sys) title("first line" + newline + "second line");
Version History
Introduced in R2012aSee Also
step | stepinfo | timeoptions
Topics
- Customize Linear Analysis Plots at Command Line (Control System Toolbox)