Generate Code from Rate-Based Model
Generate code from the rate-based model, not from the model test harness.
To generate code from a rate-based model:
In the Simulink® Toolstrip, on the Apps tab, click Embedded Coder
 .
.On the C Code tab that opens, click Build
 .
.
Code Generation Report for Rate-Based Models
The code generation report for a rate-based model describes the timing of the model.
To open the code generation report, on the C Code tab, select Open Latest Report.
Then, click Code Interface Report to view the timing of the functions in the generated code.
Generated Code Entry Points for Rate-Based Models
The combination of single-tasking versus multitasking and single-rate versus multirate controls the entry points in the generated code.
To enforce single-tasking, clear the Treat each discrete rate as a separate task configuration parameter. To allow for multitasking, select this parameter.
This table describes the generated code entry points for the
ex_rate_based_model model, which contains two atomic subsystems named
Subsystem1 and Subsystem2.
Subsystem1multiplies its input by 2.Subsystem2multiplies its input by 4.
| Configuration | Explicitly Scheduled Rates | Generated Code Entry Points |
|---|---|---|
Single-tasking or multitasking. | Single-rate.
| One entry-point function called periodically every 0.2 seconds void ex_rate_based_model_step(void)
{
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out1 = 2.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In1;
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out2 = 4.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In2;
}
|
Single-tasking. | Multirate.
| One entry-point function called periodically every 0.2 seconds. In
the entry-point function, a counter ( void ex_rate_based_model_step(void)
{
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out1 = 2.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In1;
if (ex_rate_based_model_M->Timing.TaskCounters.TID[1] == 0) {
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out2 = 4.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In2;
}
rate_scheduler();
}
The rate-scheduler function resets the counter when the entry-point function runs. static void rate_scheduler(void)
{
(ex_rate_based_model_M->Timing.TaskCounters.TID[1])++;
if ((ex_rate_based_model_M->Timing.TaskCounters.TID[1]) > 1) {
ex_rate_based_model_M->Timing.TaskCounters.TID[1] = 0;
}
} |
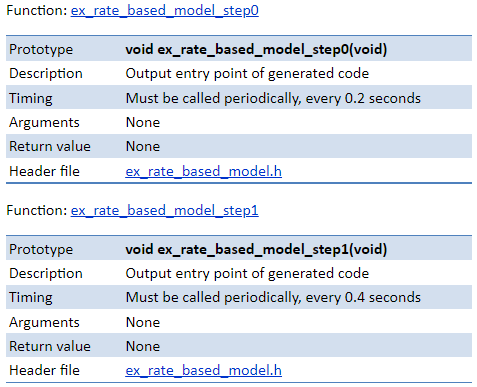
Multitasking. | Multirate.
| Two entry-point functions: one called periodically every 0.2 seconds and the other called periodically every 0.4 seconds. Rates are executed using a prioritized preemptive multitasking scheme. Faster rates are assigned higher priorities and thus executed first. void ex_rate_based_model_step0(void)
{
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out1 = 2.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In1;
}
void ex_rate_based_model_step1(void)
{
ex_rate_based_model_Y.Out2 = 4.0 * ex_rate_based_model_U.In2;
}
|