padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions
Options for generating pipeline files for Jenkins
Description
Use the padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions object to specify options
for generating Jenkins® pipeline files. To generate pipeline files, pass the object to the
padv.pipeline.generatePipeline function.
Creation
Syntax
Description
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=version)
Use
GeneratorVersion=1if you need to maintain compatibility with existing pipelines.Use
GeneratorVersion=2for new pipelines or when upgrading your pipeline setup.
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(___,PropertyName=Value)
Some properties are available in Both Versions, while other properties are specific to Version 1 Only or Version 2 Only.
Input Arguments
Pipeline generator version, specified as either:
1— Pipeline Generator Version 1 provides compatibility with the original pipeline generator functionality. UseGeneratorVersion=1if you need to maintain compatibility with existing pipelines. For more information, see Integrate Process into Jenkins.2— Pipeline Generator Version 2 contains several improvements to pipeline file propagation, generated pipeline file size, and integration with artifact management systems. UseGeneratorVersion=2for new pipelines or when upgrading your pipeline setup. For more information, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Properties
Both Versions
Jenkins agent that executes pipeline, specified as a string or string array.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 ignores this property
if the UseSameExecutorForSequentialStages property is
true.
Example: "high_memory"
Data Types: string
Specify whether Jenkins uses MATLAB Plugin to launch MATLAB, specified as either a numeric or logical 0
(false) or 1 (true).
When
0(false):Pipeline Generator Version 1 generates a pipeline that runs tasks using the specified
ShellEnvironment.Pipeline Generator Version 2 ignores the
ShellEnvironmentproperty. If the agent is a UNIX® machine, the generated pipeline uses a shell script to launch MATLAB. If the agent is not a UNIX machine, the generated pipeline uses a Windows® batch script.
When
1(true), the pipeline runs tasks using therunMATLABCommandstep from the MATLAB Plugin to launch MATLAB and the pipeline generator ignores theMatlabLaunchCmdandMatlabStartupOptionsproperties.0(false)
Note
If you dry run tasks by setting DryRun to
true in RunprocessCommandOptions, the
pipeline does not use the plugin and runs tasks using shell commands.
Data Types: logical
Command to start MATLAB program, specified as a string.
If you use a custom command to launch MATLAB on your machine, make sure to set this property. The default value of this
property is "matlab", which assumes MATLAB is available in the PATH environment variable for your
system and runs the default MATLAB executable.
The pipeline generator ignores this property when
UseMatlabPlugin is true.
Example: "C:\Program
Files\MATLAB\R2024b\bin\matlab.exe"
Data Types: string
Command-line startup options for MATLAB, specified as a string.
Use this property to specify the command-line startup options that the generated
pipeline file uses when starting the MATLAB program. By default, the pipeline generator launches MATLAB using the -batch option. If you need to run MATLAB without the -batch option, specify the property
AddBatchStartupOption as false.
Some MATLAB code, including some built-in tasks, can only run successfully if a display is available for your machine. For more information, see Set Up Virtual Display Machines Without Displays.
The pipeline generator ignores this property when
UseMatlabPlugin is true.
Example: "-nodesktop -logfile mylogfile.log"
Data Types: string
Specify whether to open MATLAB using -batch startup option, specified as a numeric or
logical 0 (false) or 1
(true).
If you need to launch MATLAB with options that are not compatible with -batch,
specify AddBatchStartupOption as false.
Data Types: logical
Number of stages and grouping of tasks in CI pipeline, specified as either:
padv.pipeline.Architecture.SingleStage— The pipeline has a single stage, named Runprocess, that runs each of the tasks in the process.
padv.pipeline.Architecture.SerialStages— The pipeline has one stage for each task iteration in the process.
padv.pipeline.Architecture.SerialStagesGroupPerTask— The pipeline has one stage for each task in the process.
padv.pipeline.Architecture.IndependentModelPipelines— The pipeline contains parallel, downstream pipelines for each model. Each downstream pipeline independently runs the tasks associated with that model. To make sure the jobs run in parallel, make sure that you either have multiple build agents available or configure your build agent to run parallel jobs.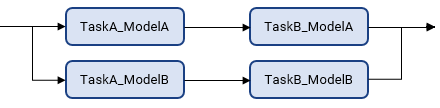
Note
You must have at least two Jenkins executors available. The pipeline generator requires one executor to
generate the pipeline and load the children stages and at least one other executor to
execute those stages. If you decide to run model tasks in parallel using the pipeline
architecture IndependentModelPipelines, you need additional
executors to handle each of the generated parallel pipelines. For information on
defining Jenkins executors, see the Jenkins documentation for Managing
Nodes.
For Pipeline Generator Version 1, if you choose a
pipeline architecture other than SingleStage, the pipeline
generator can create complex Jenkinsfile files that exceed size
limits. If Jenkins generates the error Method too large, consider
simplifying the pipeline architecture to use the SingleStage
architecture instead or upgrade to Pipeline Generator Version
2 as shown in Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
For Pipeline Generator Version 2, if you decide
to use the IndependentModelPipelines architecture to generate code
and perform code analysis tasks in parallel, you must either switch to using the
template parallel process model or update your existing process as shown in Considerations for Parallel Code Generation. These updates allow
the tasks in your pipeline to properly handle shared utilities and code generated
across parallel jobs.
Example: padv.pipeline.Architecture.IndependentModelPipelines
Example: "IndependentModelPipelines"
Options for runprocess command, specified as a
padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions object.
The object padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions has properties for each of the name-value
arguments in the runprocess
function, except for the Scope arguments
Tasks, Process,
Subprocesses, and FilterArtifact.
Note
GenerateJUnitForProcess is set to false
by default in padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions. Previously, this
property was true by default.
The GenerateJUnitForProcess property in
padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions will be removed in a future release.
Make sure to specify the GenerateJUnitForProcess property in
padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions to the value that you want the
pipeline to use.
Example: padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions()
Stop running pipeline after stage fails, specified as either:
1(true) — Stop the pipeline immediately when any stage fails.0(false) — Allow the pipeline to continue running subsequent stages, even if a previous stage fails.
If you use the built-in tasks
padv.builtin.task.RunTestsPerModel or
padv.builtin.task.RunTestsPerTestCase to run tests, keep
StopOnStageFailure set to false. This prevents
the pipeline from skipping the padv.builtin.task.MergeTestResults task if
a test stage fails.
Data Types: logical
File name of generated Jenkins pipeline file, specified as a string.
By default, the generated pipeline file generates into the subfolder derived > pipeline, relative to the project root. To change where the pipeline file
generates, specify GeneratedPipelineDirectory.
Example: "padv_generated_pipeline_file"
Data Types: string
Location where the generated pipeline file generates, specified as a string.
By default, the generated pipeline file is "simulink_pipeline".
To change the name of the generated pipeline file, specify the
GeneratedJenkinsFileName property.
Example: fullfile("derived","pipeline","test")
Data Types: string
When to collect build artifacts, specified as:
"never",0, orfalse— Never collect artifacts"on_success"— Only collect artifacts when the pipeline succeeds"on_failure"— Only collect artifacts when the pipeline fails"always",1, ortrue— Always collect artifacts
Example: "on_failure"
Data Types: logical | string
Name of ZIP file for job artifacts, specified as a string.
Example: "my_job_artifacts.zip"
Data Types: string
Generate Process Advisor build report, specified as a numeric or logical
1 (true) or 0
(false).
Data Types: logical
File format for the generated report, specified as one of these values:
"pdf"— PDF file"html"— HTML report, packaged as a zipped file that contains the HTML file, images, style sheet, and JavaScript® files of the report"html-file"— HTML report, consisting of a single HTML file that contains the text, style sheets, JavaScript, and base64-encoded images of the report"docx"— Microsoft® Word document
Name and path of generated report, specified as a string array.
By default, the report path uses a relative path to the project root and the
pipeline generator generates a report
ProcessAdvisorReport.pdf.
As a recommended practice, set the ReportPath to a sub-folder
within the project root. CI pipelines cannot archive files located in the project root
itself.
Example: "$PROJECTROOT$/PA_Results/Report/ProcessAdvisorReport"
Data Types: string
Enable integration with OpenTelemetry™ to view detailed pipeline timing and
execution data, specified as a numeric or logical true
(1) or false (0).
Before you enable the OpenTelemetry integration, you must install the OpenTelemetry-MATLAB package and set up OpenTelemetry, as shown in Collect Detailed Execution Data with OpenTelemetry Integration.
With the integration, each Jenkins build produces an OpenTelemetry trace that shows the detailed timing and execution data for each stage and step in your pipeline.
Data Types: logical
Version 1 Only
The pipeline generator does not use this property.
Enable pipeline caching to support incremental builds in CI, specified as a numeric
or logical 0 (false) or 1
(true).
For Pipeline Generator Version 1, generated
pipelines use caching by default to help the
performance of incremental builds in CI.
However, if a generated pipeline has persistent conflicts and generates errors when
merging artifact information from parallel jobs, you can disable pipeline caching by
specifying EnablePipelineCaching as 0
(false). Disabling pipeline caching increases build times, but can
help avoid merge conflicts.
Pipeline Generator Version 2 ignores this property.
Data Types: logical
Path to MATLAB installation location, specified as a string.
For Pipeline Generator Version 1, make sure the path that you specify uses the MATLAB root folder location and file separators for the operating system of your build agent.
Pipeline Generator Version 2 ignores this property.
For Pipeline Generator Version 2, make sure MATLAB is available on the system PATH so the build agent can
access MATLAB.
Example:
"C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2025b\bin"
Example:
"/usr/local/MATLAB/R2025b/bin"
Example:
"/Applications/MATLAB_R2025b.app/bin"
Data Types: string
Shell environment Jenkins uses to launch MATLAB, specified as one of these values:
"bat"— Windows batch script"sh"— Shell script"pwsh"— PowerShell Core script"powershell"— Windows PowerShell script""— Automatically use"bat"or"sh"based on the platform where pipeline generation runs
Pipeline Generator Version 2 ignores this property and instead:
If the agent is a UNIX machine, the Jenkins pipeline uses a shell script.
If the agent is not a UNIX machine, the Jenkins pipeline uses a Windows batch script.
Data Types: string
Use the same executor for sequential stages, specified as either a numeric or logical:
true(1) — By default, Pipeline Generator Version 1 configures sequential stages to use the same executor, minimizing executor usage and maintaining a shared workspace. When generating a Jenkins pipeline from a parentJenkinsfile, the sequential stages use the same executor that you defined in the top-levelnode(block of the parent'labelName')Jenkinsfileand ignore theAgentLabelproperty. For more information, see Integrate Process into Jenkins.false(0) — Pipeline Generator Version 1 configures the pipeline to allow Jenkins to release the current agent and potentially use different agents for subsequent stages. This approach can lead to smaller, more manageable jobs, but can require additional pipeline execution time. Since different agents can use different workspaces, Pipeline Generator Version 1 stores the outputs from each stage and passes those outputs to the subsequent stages. For more information on sequential stages, see the Jenkins documentation for Sequential Stages.
Pipeline Generator Version 2 ignores this property.
Data Types: logical
Version 2 Only
Path to root folder of support packages on build agent, specified as a string.
To help identify the path, you can run the function matlabshared.supportpkg.getSupportPackageRoot on the build agent.
Note
If you specify this property, you must also specify the variable
MW_SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT in your CI system.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "C:\\ProgramData\\MATLAB\\SupportPackages\\R2025a"
Data Types: string
Relative path from repository root to project root folder, specified as a string.
If your project root folder is at the repository root, leave
RelativeProjectPath as an empty string
"".
If your project is located in a subfolder, set
RelativeProjectPath to the subfolder path relative to the
repository root. The value of RelativeProjectPath must be the
portion of the project path after the repository root and must be a valid sub-path
within the full path to the project root folder. The path must end with the file
separator /.
For example:
| Situation | Project Root Folder | Valid RelativeProjectPath |
|---|---|---|
| Project in repository repo | "/home/user/repo-root" | "" |
| Project in subfolder | "/home/user/repo-root/src/myproject" | "src/myproject/" |
Note
If you specify this property, you must also specify the variable
MW_RELATIVE_PROJECT_PATH in your CI system. The path must end
with the file separator /.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "src/myproject/"
Example: "subfolder/src/myproject/"
Data Types: string
Name of remote build cache directory, specified as a string.
The pipeline generator uses the directory to store pipeline artifact caches on the
remote build cache service. The artifacts and sub-folders are inside a root folder. You
can specify the name of the root folder by using the
RemoteBuildCacheName property.
For example, inside your artifact storage location, the pipeline generator can generate a folder structure such as:
<RemoteBuildCacheName>/
└── branchName/
└── folderForEachRunId/
└── br_NameForPipelineBranch/
├── Project/
├── PA_Results/
├── derived/
│ └── artifacts.dmr
├── ir_dag.json
├── simulink_pipeline
└── __lastSuccessfulRunId__As a best practice, use a unique name for each pipeline and project to avoid conflicts between different pipelines.
Example: "Jenkins MATLAB Pipeline"
Data Types: string
Artifact storage approach, specified as one of the values in this table. The artifact service mode determines how the pipeline stores and retrieves artifact caches. Depending on which approach you choose, you must also specify the additional properties and credentials in the Requirements column.
| Value | Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
"network" | Store artifacts on a network drive | Set the |
"jfrog" | Store artifacts in a JFrog Artifactory repository | Set both the In your
CI system, save your JFrog API token as a secret with the ID
|
"s3" | Store artifacts in an Amazon S3™ bucket | Set both the In
your CI system, save your Amazon S3 access key as a secret with the ID
|
"azure_blob" | Store artifacts in an Azure® Blob Storage container | Set the In your CI system, save your Azure storage account connection string as a secret with the ID
|
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Path to network storage location for storing artifacts when
ArtifactServiceMode is "network", specified as
a string.
Specify the path to a shared network location that all agents running the pipeline can access.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "/artifactManagement/cacheStorage"
Data Types: string
URL of JFrog Artifactory server for storing artifacts when
ArtifactServiceMode is "jfrog", specified as a
string.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "http://localhost:8082/artifactory"
Data Types: string
Name of JFrog Artifactory repository for storing artifacts when
ArtifactServiceMode is "jfrog", specified as a
string.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "example-repo-local"
Data Types: string
Name of the Amazon S3 bucket for storing artifacts when ArtifactServiceMode
is "s3", specified as a string.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "my-artifacts-bucket"
Data Types: string
AWS access key ID for storing artifacts in an Amazon S3 bucket when ArtifactServiceMode is
"s3", specified as a string.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE"
Data Types: string
Name of Azure Blob Storage container for storing artifacts when
ArtifactServiceMode is "azure_blob", specified
as a string.
You can only specify a single container name, not multiple container names.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "mycontainer"
Data Types: string
Execution environment of runner, specified as either:
"default"— Runs tasks directly on the host machine without containerization."container"— Runs tasks inside a containerized environment, such as a Docker® container. Specify the container by using theImageTagproperty.The container does not use MATLAB actions. Make sure to specify the
UseMatlabPlugin,MatlabLaunchCmd,MatlabStartupOptions, andAddBatchStartupOptionproperties as required by your setup. For example:op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=2); % Docker image settings op.UseMatlabPlugin = false; op.MatlabLaunchCmd = "xvfb-run -a matlab -batch"; op.MatlabStartupOptions = ""; op.AddBatchStartupOption = false;
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Full name of the container image that the generated pipeline uses when
RunnerType is "container", specified as a
string. Optionally, you can specify arguments for the container image by using the
ImageArgs property.
The image must be an OCI-compliant image, such as a Docker image.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "mycompany/pipeline-runner:latest"
Data Types: string
Arguments for container image that the generated pipeline uses when
RunnerType is "container", specified as a
string.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: "-e
MLM_LICENSE_FILE=27000@MyLicenseServer"
Data Types: string
Branches to check for cached build artifacts, specified as a string.
To support incremental builds, the pipeline generator attempts
to restore the cache from the last successful run on the same branch. If no cache is available,
the pipeline checks for cached build artifacts on the branches that you specify. By default, the
fallback branch is main, but you can specify multiple fallback branches and
the pipeline checks each one in order. If the pipeline generator does not find a cache on the
specified branches, the pipeline runs a full build, executing each task in the process without
skipping tasks. For more information, see How Pipeline Generation Works.
Pipeline Generator Version 1 does not support this property.
Example: ["develop"]
Example: ["main","develop"]
Data Types: string
Examples
This example code shows how to generate a Jenkins pipeline file in MATLAB using Pipeline Generator Version 1. However, typically, you configure your options object and call the pipeline generator from inside a Jenkins CI pipeline file. For a complete example, see Integrate Process into Jenkins.
Note
Pipeline Generator Version 1 is provided for compatibility with the original pipeline generator functionality. Pipeline Generator Version 2 is recommended for enhanced file propagation and artifact management, but requires you to update your setup and workflow.
Load a project. For this example, you can load a Process Advisor example project.
processAdvisorExampleStart
Represent your pipeline generator options by creating a
padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions object for pipeline generator version
1.
op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=1);
Generate a pipeline file.
padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(op)
simulink_pipeline, for the current
project, process model, and pipeline generator options.This example code shows how to configure and generate a Jenkins pipeline file using Pipeline Generator Version 2 and network artifact storage. For the complete example, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Inside your generate_jenkins_pipeline.m file, you can use a
shared network location for your artifacts by specifying the
NetworkStoragePath property. For this example, suppose you have a
shared network location
/artifactManagement/cacheStorage.
% Copyright 2025 The MathWorks, Inc. function generate_jenkins_pipeline() workspace = string(getenv('WORKSPACE')); supportPackageRoot = string(getenv('MW_SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT')); relativeProjectPath = string(getenv('MW_RELATIVE_PROJECT_PATH')); remoteBuildCacheName = string(getenv('MW_REMOTE_BUILD_CACHE_NAME')); pipelineGenDirectory = string(getenv('MW_PIPELINE_GEN_DIRECTORY')); cp = openProject(strcat(workspace,filesep,string(relativeProjectPath))); op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions; op.AgentLabel = "my-jenkins-agent-label"; op.PipelineArchitecture = "SerialStagesGroupPerTask"; op.GeneratorVersion = 2; op.SupportPackageRoot = supportPackageRoot; op.GeneratedPipelineDirectory = pipelineGenDirectory; op.StopOnStageFailure = true; op.RunprocessCommandOptions.GenerateJUnitForProcess = true; op.ReportPath = "$PROJECTROOT$/PA_Results/Report/ProcessAdvisorReport"; op.RelativeProjectPath = relativeProjectPath; op.RemoteBuildCacheName = remoteBuildCacheName; op.ArtifactServiceMode = 'network'; op.NetworkStoragePath = '/artifactManagement/cacheStorage'; padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(op, "CIPipeline"); end
"my-jenkins-agent-label".This example code shows how to configure and generate a Jenkins pipeline file using Pipeline Generator Version 2 and JFrog Artifactory. For the complete example, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Inside your generate_jenkins_pipeline.m file, you can use a JFrog
Artifactory repository for your artifacts by specifying the
ArtifactServiceMode property as "jfrog" and
specifying the properties ArtifactoryUrl and
ArtifactoryRepoName.
% Copyright 2025 The MathWorks, Inc. function generate_jenkins_pipeline() workspace = string(getenv('WORKSPACE')); supportPackageRoot = string(getenv('MW_SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT')); relativeProjectPath = string(getenv('MW_RELATIVE_PROJECT_PATH')); remoteBuildCacheName = string(getenv('MW_REMOTE_BUILD_CACHE_NAME')); pipelineGenDirectory = string(getenv('MW_PIPELINE_GEN_DIRECTORY')); cp = openProject(strcat(workspace,filesep,string(relativeProjectPath))); op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions; op.AgentLabel = "my-jenkins-agent-label"; op.PipelineArchitecture = "SerialStagesGroupPerTask"; op.GeneratorVersion = 2; op.SupportPackageRoot = supportPackageRoot; op.GeneratedPipelineDirectory = pipelineGenDirectory; op.StopOnStageFailure = true; op.RunprocessCommandOptions.GenerateJUnitForProcess = true; op.ReportPath = "$PROJECTROOT$/PA_Results/Report/ProcessAdvisorReport"; op.RelativeProjectPath = relativeProjectPath; op.RemoteBuildCacheName = remoteBuildCacheName; op.ArtifactServiceMode = 'jfrog'; op.ArtifactoryUrl = 'http://localhost:8082/artifactory'; op.ArtifactoryRepoName = 'example-repo-local'; padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(op, "CIPipeline"); end
"my-jenkins-agent-label".This example code shows how to configure and generate a Jenkins pipeline file using Pipeline Generator Version 2 and Amazon S3 storage. For the complete example, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Inside your generate_jenkins_pipeline.m file, you can use
Amazon S3 storage for your artifacts by specifying the
ArtifactServiceMode property as "s3" and
specifying the properties S3BucketName and
S3AwsAccessKeyID.
% Copyright 2025 The MathWorks, Inc. function generate_jenkins_pipeline() workspace = string(getenv('WORKSPACE')); supportPackageRoot = string(getenv('MW_SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT')); relativeProjectPath = string(getenv('MW_RELATIVE_PROJECT_PATH')); remoteBuildCacheName = string(getenv('MW_REMOTE_BUILD_CACHE_NAME')); pipelineGenDirectory = string(getenv('MW_PIPELINE_GEN_DIRECTORY')); cp = openProject(strcat(workspace,filesep,string(relativeProjectPath))); op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions; op.AgentLabel = "my-jenkins-agent-label"; op.PipelineArchitecture = "SerialStagesGroupPerTask"; op.GeneratorVersion = 2; op.SupportPackageRoot = supportPackageRoot; op.GeneratedPipelineDirectory = pipelineGenDirectory; op.StopOnStageFailure = true; op.RunprocessCommandOptions.GenerateJUnitForProcess = true; op.ReportPath = "$PROJECTROOT$/PA_Results/Report/ProcessAdvisorReport"; op.RelativeProjectPath = relativeProjectPath; op.RemoteBuildCacheName = remoteBuildCacheName; op.ArtifactServiceMode = 's3'; op.S3BucketName = 'my-artifacts-bucket'; op.S3AwsAccessKeyID = 'AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE'; padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(op, "CIPipeline"); end
"my-jenkins-agent-label".This example code shows how to configure and generate a Jenkins pipeline file using Pipeline Generator Version 2 and Azure Blob Storage. For the complete example, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Inside your generate_jenkins_pipeline.m file, you can use
Azure Blob Storage for your artifacts by specifying the
ArtifactServiceMode property as "azure_blob"
and specifying the property
AzContainerName.
% Copyright 2025 The MathWorks, Inc. function generate_jenkins_pipeline() workspace = string(getenv('WORKSPACE')); supportPackageRoot = string(getenv('MW_SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT')); relativeProjectPath = string(getenv('MW_RELATIVE_PROJECT_PATH')); remoteBuildCacheName = string(getenv('MW_REMOTE_BUILD_CACHE_NAME')); pipelineGenDirectory = string(getenv('MW_PIPELINE_GEN_DIRECTORY')); cp = openProject(strcat(workspace,filesep,string(relativeProjectPath))); op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions; op.AgentLabel = "my-jenkins-agent-label"; op.PipelineArchitecture = "SerialStagesGroupPerTask"; op.GeneratorVersion = 2; op.SupportPackageRoot = supportPackageRoot; op.GeneratedPipelineDirectory = pipelineGenDirectory; op.StopOnStageFailure = true; op.RunprocessCommandOptions.GenerateJUnitForProcess = true; op.ReportPath = "$PROJECTROOT$/PA_Results/Report/ProcessAdvisorReport"; op.RelativeProjectPath = relativeProjectPath; op.RemoteBuildCacheName = remoteBuildCacheName; op.ArtifactServiceMode = 'azure_blob'; op.AzContainerName = 'mycontainer'; padv.pipeline.generatePipeline(op, "CIPipeline"); end
"my-jenkins-agent-label".Version History
Starting in February 2026, the template file,
Jenkinsfile_pipeline_gen, for pipeline generator version 2 uses the
Git™ submodule checkout behavior that you define in the SCM
section of the Jenkins Pipeline configuration page.
Since Jenkins manages submodule checkout behavior directly at the SCM level,
padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions does not have a
CheckoutSubmodules property.
To configure submodule checkout behavior, open the SCM section of the Jenkins Pipeline configuration page. Under Additional Behaviours, add Advanced sub-modules behaviours and enable Recursively update submodules. For more information, see the Jenkins documentation for Advanced sub-modules behaviours.
To access the updated Jenkinsfile_pipeline_gen template file in
MATLAB,
enter:
copyfile(fullfile(matlabshared.supportpkg.getSupportPackageRoot, ... "toolbox/padv/samples/jenkinsV2/auto_gen/Jenkinsfile_pipeline_gen"));
Starting in October 2025, the setup and requirements for pipeline generator 2 have changed. Update your setup and code as shown in Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins.
Previously, you provided configuration details using environment variables. Now, you
must specify these details as properties of your pipeline generation options object,
padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions.
| Previous Environment Variable | Use This padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions Property Instead |
|---|---|
env.PYTHON_ALIAS | No longer used. The pipeline generator expects the alias
|
env.SUPPORT_PACKAGE_ROOT | SupportPackageRoot |
env.ARTIFACT_SERVICE_MODE | ArtifactServiceMode |
env.NETWORK_STORAGE_PATH | NetworkStoragePath |
env.PATH | No longer used. Make sure MATLAB is available on the system |
Starting in October 2025, Pipeline Generator Version 2 supports generating pipelines that use a specific container image. For example:
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=2); options.RunnerType = "container"; options.ImageTag = "mycompany/docker-pipeline-runner:latest";
Starting in October 2025, Pipeline Generator Version 2 supports storing artifacts in:
Amazon S3 buckets. For example:
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=2); options.ArtifactServiceMode = "s3"; options.S3AwsAccessKeyID = "AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE"; options.S3BucketName = "my-artifacts-bucket";
Azure Blob Storage containers. For example:
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=2); options.ArtifactServiceMode = "azure_blob"; options.AzContainerName = "mycontainer";
Starting in October 2025, Pipeline Generator Version 2
supports projects where the project root folder is in a subfolder of the repository root.
Specify the relative path from the repository root to your project by using the
RelativeProjectPath
property.
options = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GeneratorVersion=2); % Suppose the full path to the project root is: % "/home/user/repo-root/src/myproject" options.RelativeProjectPath = "src/myproject";
Starting in April 2025, the CI Support Package for Simulink® includes version 2 of the pipeline generator. Pipeline Generator Version 2 includes enhanced features like external artifact management with JFrog Artifactory.
To upgrade to version 2, see Process Integration and Artifact Management for Jenkins. Otherwise, specify the
GeneratorVersion property as 1 to keep the
original pipeline generator functionality.
The property GenerateJUnitForProcess will be removed in a future
release.
To control how generated pipelines invoke the runprocess function,
use the RunprocessCommandOptions property instead.
| Functionality | Use This Instead |
|---|---|
op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(GenerateJUnitForProcess=false) |
rpo = padv.pipeline.RunProcessOptions; rpo.GenerateJUnitForProcess = false; op = padv.pipeline.JenkinsOptions(RunprocessCommandOptions=rpo) |
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)