padv.TaskTool
Description
A padv.TaskTool object represents a tool that you
can add to your task or process to help you organize and complete task activities in
Process Advisor. Starting in R2023b, your task tools are available from the
options menu for a task in Process Advisor.
You
add the task tool to your process model by using the addTaskTool
function and link the tool to a specific task or process by setting the
TaskTools property of the task or process. In Process
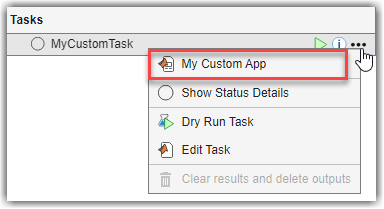
Advisor, you access task tools by pointing to the task in the
Tasks column and opening the options menu (...).
Creation
Syntax
Description
padv.TaskTool(ToolFunction= creates a task tool that represents a custom app that you can open from the task
options menu in Process Advisor. You design the app by using App
Designer or AppName,Title=Title,Type="TaskApp")
uifigure.
padv.TaskTool(ToolFunction= creates a task tool that represents a command that you can run from the task
options menu in Process Advisor.FunctionName,Title=toolTitle,Type="Command")
padv.TaskTool(___,Arguments= passes arguments to the task
tool. For example,
Arguments)
padv.TaskTool(ToolFunction="blankApp1",Title="My Custom
App",Type="TaskApp",Arguments="arg1") passes the argument
arg1 to the task app.
Input Arguments
Name of app to open, specified as a string. Do not include the file extension.
The app must:
Be an app that you design using App Designer or
uifigure. You can save the app as an App Designer app (.mlapp), export the App Designer app as an M file, or define the app by using a MATLAB® class (.m).Be on the MATLAB path.
Include a
TaskContextproperty that you pass as a name-value argument in the constructor. Process Advisor uses the argument to identify the context of the task in your process.Do one of the following during initialization:
For example, the following MATLAB class defines a blank task app.
classdef blankApp1 < matlab.apps.AppBase properties (Access = public) UIFigure matlab.ui.Figure TaskContext end methods (Access = private) function createComponents(app) app.UIFigure = uifigure('Visible', 'on'); end end methods (Access = public) function app = blankApp1(NameValueArgs) arguments NameValueArgs.TaskContext end app.TaskContext = NameValueArgs.TaskContext; createComponents(app); if nargout == 0 clear app end end function delete(app) delete(app.UIFigure) end end end
For an example App Designer file, see
TaskAppDemo.mlapp in the Process Advisor example
project shown in Integrate Custom App into Process Advisor.
Example: "blankApp1"
Data Types: string
Name of function to evaluate, specified as a string. Do not include the file extension.
The function must accept a TaskContext as a name-value
argument in its NameValueArgs input. Process Advisor
uses this argument to identify the context of the task in your process. Inside the
function, specify the command that you want the task tool to
execute.
function out = myTaskCommand(NameValueArgs) arguments NameValueArgs.TaskContext end % define task command here end
padv.TaskTool uses the feval function to evaluate the function and
any input arguments that you specify in
padv.TaskTool.
For an example, see Integrate Custom Commands into Process Advisor.
Example: "myTaskCommand"
Data Types: string
Tool name that appears in Process Advisor app, specified as a string.
Example: "My Custom App"
Data Types: string
Input arguments for tool, specified as a cell array.
Example: {'arg1'}
Example: {"arg1","arg2"}
Data Types: cell
Properties
Name of app to open or function to evaluate, specified as a string. Do not include the file extension.
The value that you specify depends on the type of task app that you create:
If the
Typeproperty is"TaskApp", specify the name of an app. The app must:Be an app that you design by using App Designer or
uifigure.Be on the MATLAB path.
Include a
TaskContextproperty that you pass as a name-value argument in the constructor. Process Advisor uses the argument to identify the context of the task in your process.Do one of the following during initialization:
For example, the following MATLAB class defines a blank task app.
classdef blankApp1 < matlab.apps.AppBase properties (Access = public) UIFigure matlab.ui.Figure TaskContext end methods (Access = private) function createComponents(app) app.UIFigure = uifigure('Visible', 'on'); end end methods (Access = public) function app = blankApp1(NameValueArgs) arguments NameValueArgs.TaskContext end app.TaskContext = NameValueArgs.TaskContext; createComponents(app); if nargout == 0 clear app end end function delete(app) delete(app.UIFigure) end end end
For an example App Designer file, see
TaskAppDemo.mlappin the Process Advisor example project shown in Integrate Custom App into Process Advisor.If the
Typeproperty is"Command", specify the name of a function to evaluate. The function must accept aTaskContextas a name-value argument in itsNameValueArgsinput. Process Advisor uses this argument to identify the context of the task in your process.Inside the function, specify the command that you want the task tool to execute.
function out = myTaskCommand(NameValueArgs) arguments NameValueArgs.TaskContext end % define task command here end
padv.TaskTooluses thefevalfunction to evaluate the function and any input arguments that you specify inpadv.TaskTool.For an example, see Integrate Custom Commands into Process Advisor.
Example: "blankApp1"
Example: "fun"
Data Types: string
Tool name that appears in Process Advisor app, specified as a string.
Example: "My Custom App"
Data Types: string
Type of tool, specified as either:
padv.TaskToolType.TaskApp— Represents a custom app that you can open from the task options menu in Process Advisor. You can design the app by using App Designer oruifigure. Use this type to represent interactive apps that you create for your tasks.padv.TaskToolType.Command— Represents a command that you can run from the task options menu in Process Advisor. Use this type to represent programmatic commands that you execute.
These values belong to the enumeration class
padv.TaskToolType.
Example: padv.TaskToolType.TaskApp
Input arguments for tool, specified as a cell array.
Example: {'arg1'}
Example: {"arg1","arg2"}
Data Types: cell
Examples
Starting in R2023b, you can integrate custom apps into your process
model. You create the custom app by using App
Designer or uifigure and then represent the app by
using a padv.TaskTool object. You add the custom app to your task and
process model by using the addTaskTool
function and the TaskTools property. You can use these custom apps to
provide a UI to help you perform and complete activities for a task in your process.
For this example, you modify a custom task app in App Designer to display the commit history of the model and access the task app in Process Advisor.
Open the Process Advisor example project.
processAdvisorExampleStart
Open the standalone Process Advisor window.
processAdvisorWindow
Open the Additional Examples process by selecting Additional Examples from the Process gallery in the toolstrip. The Additional Examples process contains example tasks that use a custom task app created in App Designer.

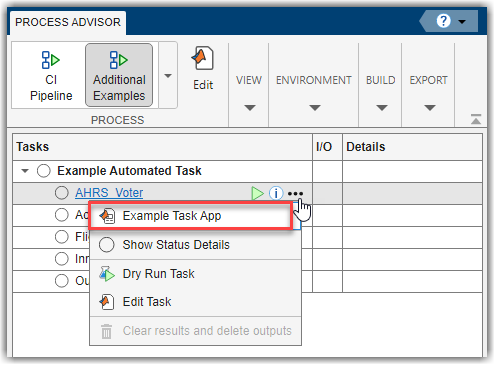
In the Tasks column, expand the task Example Automated
Task and open the task app for the AHRS_Voter model by
pointing to AHRS_Voter, opening the task options menu
(...), and clicking Example Task
App.
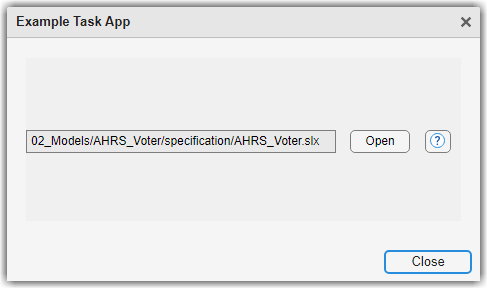
The App Designer app opens inside Process Advisor. The Example
Task App dialog box shows the relative path to the model and several buttons for
interacting with the app. The dialog box was designed in App Designer and
provides a UI for opening a model and accessing other options using App
Designer UI components. For example, you can open the current task iteration
artifact, AHRS_Voter, by clicking Open in the
Example Task App dialog box.
In Process Advisor, close the Example Task App dialog box by clicking Close.
In the project root, find the example app, TaskAppDemo.mlapp, and
the example function, exampleProcess.m.
The exampleProcess function defines a
padv.TaskTool object for the task app and adds the
padv.TaskTool object, appOpenModel, to the
example task and process model. Since the tool function is an App Designer
app, the Type is set to
padv.TaskToolType.TaskApp. The ToolFunction
argument specifies the App Designer file name,
TaskAppDemo, that defines the example task app
UI.
% Example Task App appOpenModel = padv.TaskTool( ... Title = "Example Task App", ... Type = padv.TaskToolType.TaskApp, ... ToolFunction = "TaskAppDemo"); pm.addTaskTool(appOpenModel); ... taskExampleTaskApps.TaskTools = appOpenModel;
Open and inspect the exampleProcess.m file to view the full code.
The processmodel.m file calls the exampleProcess
function on the process model object, pm, to add the example process
to the process model for the project.
Open the example task app in App Designer by double-clicking the
TaskAppDemo.mlapp file in the root of the example project. You
can use App Designer to interactively develop the example task app. For more
information, see App Designer.
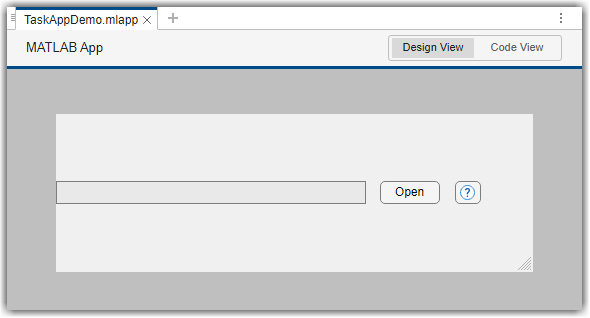
In App Designer, drag and drop a Table UI component onto the canvas. Resize the table and app layout as needed.
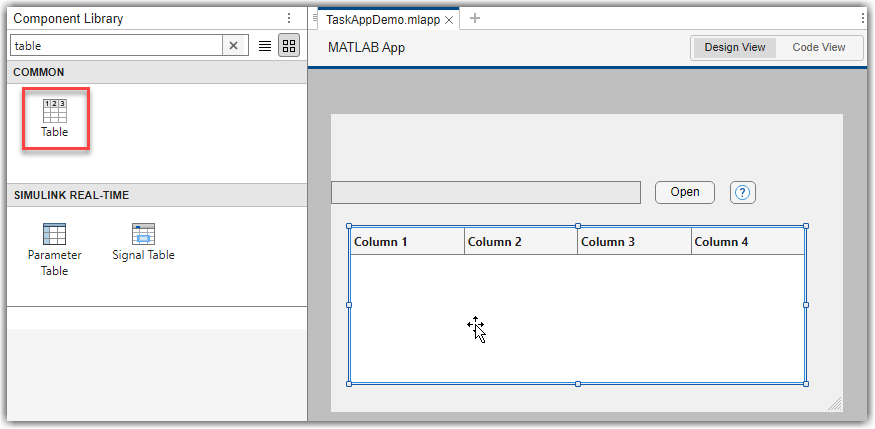
View the app code by clicking the Code View button above the
canvas. This example app uses a startup function, startupFcn, to find
the task context object, extract the task iteration artifact, and display the model file
path in the app. When you open a task app, Process Advisor passes a padv.TaskContext object to the task
app.
function startupFcn(app, varargin) % Find the TaskContext object in varargin taskContextIndex = find(cellfun(@(x) isa(x, 'padv.TaskContext'), varargin), 1); if ~isempty(taskContextIndex) app.TaskContext = varargin{taskContextIndex}; % Get the IterationArtifact iterationArtifact = app.TaskContext.getIterationArtifact(); % Get the file path from the name field filePath = iterationArtifact.name; app.ModelFilePath.Value = filePath; end end
In the conditional block within startupFcn, add code that retrieves
and displays the commit history for the current task iteration artifact in the table
component of the app, app.UITable. The following code shows the
updated startupFcn
function.
function startupFcn(app, varargin) % Find the TaskContext object in varargin taskContextIndex = find(cellfun(@(x) isa(x, 'padv.TaskContext'), varargin), 1); if ~isempty(taskContextIndex) app.TaskContext = varargin{taskContextIndex}; % Get the IterationArtifact iterationArtifact = app.TaskContext.getIterationArtifact(); % Get the file path from the name field filePath = iterationArtifact.name; app.ModelFilePath.Value = filePath; % Display commit history for iteration artifact repo = gitrepo; commitHistory = log(repo.CurrentBranch,File=filePath); app.UITable.Data = commitHistory; columnNames = commitHistory.Properties.VariableNames; app.UITable.ColumnName = columnNames; end end
In Process Advisor, update the task information by clicking
Refresh Tasks and open the task app for
AHRS_Voter. The Example Task App dialog box shows a table with
the commit message, branches, and authoring information for the
AHRS_Voter model.

Starting in R2023b, you can integrate custom commands into your
process model by using the addTaskTool
function and TaskTools property. You represent the custom commands by
using padv.TaskTool objects. For this example, you add two custom
commands as tools for a task and view the tools in the options menu for the task in
Process Advisor.
Open the Process Advisor example project. The model AHRS_Voter opens with the Process Advisor pane to the left of the Simulink® canvas.
processAdvisorExampleStart
Define your custom command by creating a new MATLAB function file. The function must accept a TaskContext as a name-value argument and must be on the MATLAB path.
For this example, you can create a file named taskCmd1.m and define a
custom function that accepts and displays an input
argument.
function out = taskCmd1(inputArg, NamedValueArgs) arguments inputArg NamedValueArgs.TaskContext end disp(inputArg); end
In the Process Advisor pane, click the Edit process model ![]() button to open the
button to open the processmodel.m file for the project.
Replace the contents of the processmodel.m file with the following example
code. The code defines:
myTask— A custom task.myTaskTool— A custom tool for a task. The tool calls the function specified by theToolFunctionargument. In the Process Advisor context menu for a task, the tool has the titleMy Command 1. Since the tool function,taskCmd1, is a.mfile for a function that defines a command for the task tool to execute, theTypeis set toCommand. The function accepts an input argumentcmd1Arg.
Inside the process model, the code adds the task and tool to the process model and specifies the tool as one of the task tools for the task.
function processmodel(pm) % Define process model for project arguments pm padv.ProcessModel end % --- Task --- myTask = padv.Task("MyTask"); pm.addTask(myTask); % --- TaskTool --- cmd1Arg = "myInputArg"; myTaskTool = padv.TaskTool(ToolFunction="taskCmd1",... Title="My Command 1",... Type=padv.TaskToolType.Command,... Arguments={cmd1Arg}); % --- Integrate --- pm.addTaskTool(myTaskTool); myTask.TaskTools = myTaskTool; end
In Process Advisor, update the task information by clicking Refresh Tasks.
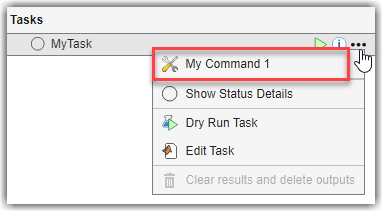
In the Tasks column, point to MyTask, open the options menu (...), and click My Command 1.
Process Advisor executes the command specified in the taskCmd1 function. The function displays the input argument, "myInputArg", in the MATLAB Command Window.
Version History
Introduced in R2023b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)