Configure Simulink Template for Drift-Aware Incremental Learning
This example shows how to configure the Simulink® Template for Drift-Aware Incremental Learning template to perform drift-aware incremental linear classification.
Overview
Drift-aware learning combines incremental learning, or online learning with the ability to perform concept drift detection. Given incoming data from a data stream, the drift-aware model resets the internal parameters of the incremental models if it detects the performance of the model is drifting. This template combines the use of the built-in Incremental Fit, Per Observation Loss and Detect Drift blocks along with DataStoreMemory blocks and custom subsystems to create a drift-aware learning workflow in Simulink. While this template uses the
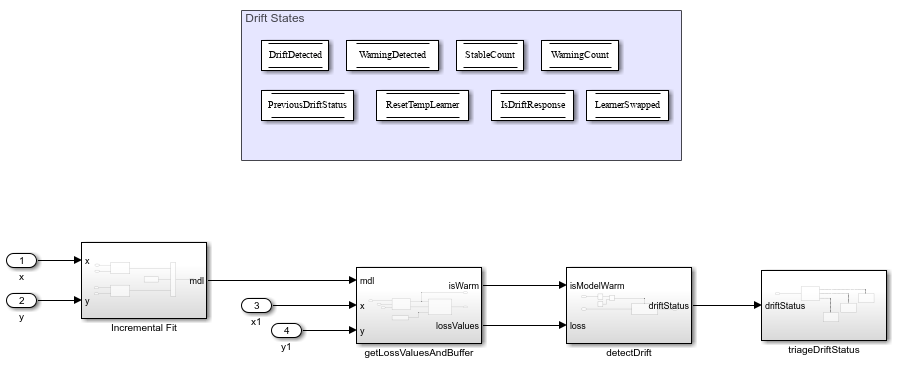
The template needs the following inputs and workspace variables:
Variable name | Usage location | Function |
| Inport 1 and 2 | Streaming input data to train the incremental model |
| Inport 3 and 4 | Streaming test data to compute loss values that are checked for drift |
| Incremental Fit subsystem | An incremental classification or regression model object |
| getLossValuesAndBuffer subsystem | A drift-aware incremental classification or regression model object |
| detectDrift subsystem | An |
| getLossValuesAndBuffer > updateBuffer block | Size of buffer to store loss values |
| triageDriftstatus > driftIsWarning > If Action subsystem | Maximum number of consecutive |
Subsystems
There are four subsystems in the template:
Incremental Fit
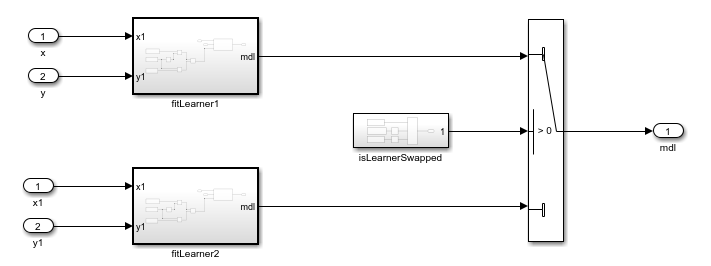
This subsystem trains 2 learners - a base learner and a temporary learner using the streaming input data. If the subsequent subsystems detect a drift using the trained learner, the system swaps the base learner with the temporary learner and resets the temporary learner.
2. getLossValuesAndBuffer

This subsystem calculates the per-obervation loss using the trained incremental model using the Per Observation Loss block. The MATLAB function block, updateBuffer, stores the loss values into a buffer of BufferSize.
3. detectDrift
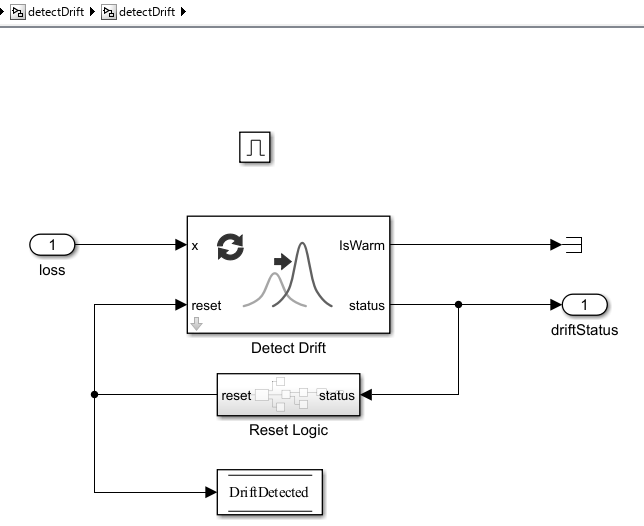
This subsystem checks for drift in the loss values. If drift is detected, i.e. status = 2, the drift detector is reset. The reset signal is also stored in the DriftDetected datastore block.
4. triageDriftStatus

This subsystem updates various datastore values based on the driftStatus. If the driftStatus is:
stable- the warning count is set to0, stable count is incremented and the temporary learner is discarded.warning- the warning count is incremented by 1 and checked against the warning count limit. If it violates the limit, then a drift is detected. If it does not violate a limit, the system continues training the temporary learner.drift- the base learner takes the value of the temporary learner and the temporary learner is reset. The warning count is set to0.
Apart from subsystems, the datastore memory blocks (DriftDetected, WarningDetected, StableCount etc.) are utilized for transfer of drift state information across the various subsytems. For a detailed explanation of the algorithm, see Algorithms.
In this example, you will do the following:
Create train and test input data to simulate streaming data for the Simulink Inport blocks of the template.
Create a binary linear classification model for incremental drift-aware learning.
Load the template and configure the template properties such as port dimensions.
Run the drift-aware workflow in Simulink.
Load and Preprocess Input Data for Simulink
Load the human activity data set and randomly shuffle the data.
load humanactivity n = numel(actid); % Number of observations p = size(feat,2); % Number of predictors rng(0,"twister") % For reproducibility idx = randsample(n,n); X = feat(idx,:); Y = actid(idx);
For details on the data set, enter Description at the command line.
The data has 60 predictors (p) and 24,075 observations (n). Responses can be one of five classes: Sitting, Standing, Walking, Running, or Dancing. Dichotomize the response by identifying whether the subject is moving (actid > 2).
Y = Y > 2;
Simulate streaming data by dividing the training data into chunks of 50 observations. For each chunk, select a single observation as a test set.
numObsPerChunk = 50; nchunk = floor(n/numObsPerChunk); for j = 1:nchunk ibegin = min(n,numObsPerChunk*(j-1) + 1); iend = min(n,numObsPerChunk*j); idx = ibegin:iend; Xin(:,:,j) = X(idx,:); Yin(:,j) = Y(idx); Xtest(1,:,j) = X(idx(1),:); Ytest(1,j) = Y(1); end
Convert the training and test set chunks into time series objects.
k = size(Xin,3); % Number of data chunks
t = 0:k-1;
Xin_ts = timeseries(Xin,t,InterpretSingleRowDataAs3D=true);
Yin_ts = timeseries(Yin',t,InterpretSingleRowDataAs3D=true);
Xtest_ts = timeseries(Xtest,t,InterpretSingleRowDataAs3D=true);
Ytest_ts = timeseries(Ytest',t,InterpretSingleRowDataAs3D=true);Create workspace variables and objects
Create an incremental classification linear model for binary classification. Specify that the data has p predictors and the data type of the responses is logical. Standardize the data using an estimation period of 500 observations. Create a workspace variable linearMdl to store the initial incremental learning model and driftAwareMdl to use in the Per Observation Loss block in the getLossValuesAndBuffer subsystem .
Mdl = incrementalClassificationLinear(NumPredictors=p, ...
ClassNames=[false,true],Standardize=true,EstimationPeriod=500);
driftAwareMdl = Mdl;
linearMdl = Mdl;Create an IncCDDetector workspace variable with the concept drift detector with the "hddma" detection method, along with BufferSize for the loss values buffer and WarningCountLimit for the limit on warnings before drift is detected.
IncCDDetector = incrementalConceptDriftDetector("hddma");
BufferSize = 1000;
WarningCountLimit = 5;Load and Configure Template
Load the Drift-Aware Training for Incremental Learning template. The template is also available on the Simulink Start Page under Statistics and Machine Learning.
template = Simulink.createFromTemplate("drift_aware_classif.sltx");
open_system(template)Click the Simulink template canvas to select it as the current system. The template contains four inport blocks: x, y, x1, and y1. Enable external input to use the streaming data Xin_ts, Yin_ts, X_ts and Y_ts as inputs to the Incremental Fit and getLossValuesandBuffer subsystem blocks.
set_param(gcs,LoadExternalInput="on") set_param(gcs,ExternalInput="Xin_ts,Yin_ts,Xtest_ts,Ytest_ts")
Configure the port dimensions of the predictor data inport blocks for the Incremental Fit block and getLossValuesAndBuffer (x and x1) as [numObsPerChunk,p] and [1,p]. Specify their output data type as double.
% x xNamePath = [gcs,'/x']; set_param(xNamePath,PortDimensions= ... "["+num2str(numObsPerChunk)+","+num2str(p)+"]", OutDataTypeStr="double"); % x1 x1NamePath = [gcs,'/x1']; set_param(x1NamePath,PortDimensions= ... "["+'1'+","+num2str(p)+"]",OutDataTypeStr="double");
Configure the port dimensions of the label data inport blocks for the Incremental Fit block and getLossValuesAndBuffer (y and y1) as [numObsPerChunk] and [1]. Specify their output data type as boolean.
% y yNamePath = [gcs,'/y']; set_param(yNamePath,PortDimensions=num2str(numObsPerChunk),OutDataTypeStr="boolean") % y1 y2NamePath = [gcs,'/y1']; set_param(y2NamePath,PortDimensions=num2str(1),OutDataTypeStr="boolean")
Set the simulation stop time to the number of data chunks times the number of inport blocks.
set_param(gcs,SolverType="Fixed-step")
set_param(gcs,StopTime=num2str(k*5))Simulate Model
Click the Run button in the Simulink model to perform drift-aware incremental learning.
See Also
IncrementalClassificationLinear Fit | Detect Drift | Per Observation Loss