Results for
- Use the new exportapp function to capture an image of your app|uifigure
- MATLAB's getframe now supports apps & uifigures
- Review: How to get the handle to an app figure
Use the new exportapp function to capture an image of your app|uifigure
Imagine these scenarios:
- Your app contains several adjustable parameters that update an embedded plot and you'd like to remember the values of each app component so that you can recreate the plot with the same dataset
- You're constructing a manual for your app and would like to include images of your app
- You're app contains a process that automatically updates regularly and you'd like to store periodic snapshots of your app.
As of MATLABs R2020b release , we no longer must rely on 3rd party software to record an image of an app or uifigure.
exportapp(fig,filename) saves an image (JPEG | PNG | TIFF | PDF) of a uifigure ( fig) with the specified file name or full file path ( filename). MATLAB's documentation includes an example of how to add an [Export] button to an app that allows the user to select a path, filename, and extension for their exported image.
Here's another example that merely saves the image as a PDF to the app's main folder.
1. Add a button to the app and assign a ButtonPushed callback function to the button. This one also assigns an icon to the button in the form of an svg file.

2. Define the callback function to name the image after the app's name and include a datetime stamp. The image will be saved to the app's main folder.
% Button pushed function: SnapshotButton
function SnapshotButtonPushed(app, ~)
% create filename containing the app's figure name (spaces removed)
% and a datetime stamp in format yymmdd_hhmmss
filename = sprintf('%s_%s.pdf',regexprep(app.MyApp.Name,' +',''), datestr(now(),'yymmdd_HHMMSS'));
% Get the app's path
filepath = fileparts(which([mfilename,'.mlapp']));
% Store snapshot
exportapp(app.MyApp, fullfile(filepath,filename))
end
Matlab's getframe now supports apps & uifigures
getframe(h) captures images of axes or a uifigure as a structure containing the image data which defines a movie frame. This function has been around for a while but as of r2020b , it now supports uifigures. By capturing consecutive frames, you can create a movie that can be played back within a Matlab figure (using movie ) or as an AVI file (using VideoWriter ). This is useful when demonstrating the effects of changes to app components.
The general steps to recording a process within an app as a movie are,
1. Add a button or some other event to your app that can invoke the frame recording process.
2. Animation is typically controlled by a loop with n iterations. Preallocate the structure array that will store the outputs to getframe. The example below stores the outputs within the app so that they are available by other functions within the app. That will require you to define the variable as a property in the app.
% nFrames is the number of iterations that will be recorded.
% recordedFrames is defined as a private property within the app
app.recordedFrames(1:nFrames) = struct('cdata',[],'colormap',[]);
3. Call getframe from within the loop that controls the animation. If you're using VideoWriter to create an AVI file, you'll also do that here (not shown, but see an example in the documentation ).
% app.myAppUIFigure: the app's figure handle % getframe() also accepts axis handles for i = 1:nFrames
... % code that updates the app for the next frame
app.recordedFrames(i) = getframe(app.myAppUIFigure); end
4. Now the frame data are stored in app.recordedFrames and can be accessed from anywhere within the app. To play them back as a movie,
movie(app.recordedFrames) % or movie(app.recordedFrames, n) % to play the movie n-times movie(app.recordedFrames, n, fps) % to specify the number of frames per second
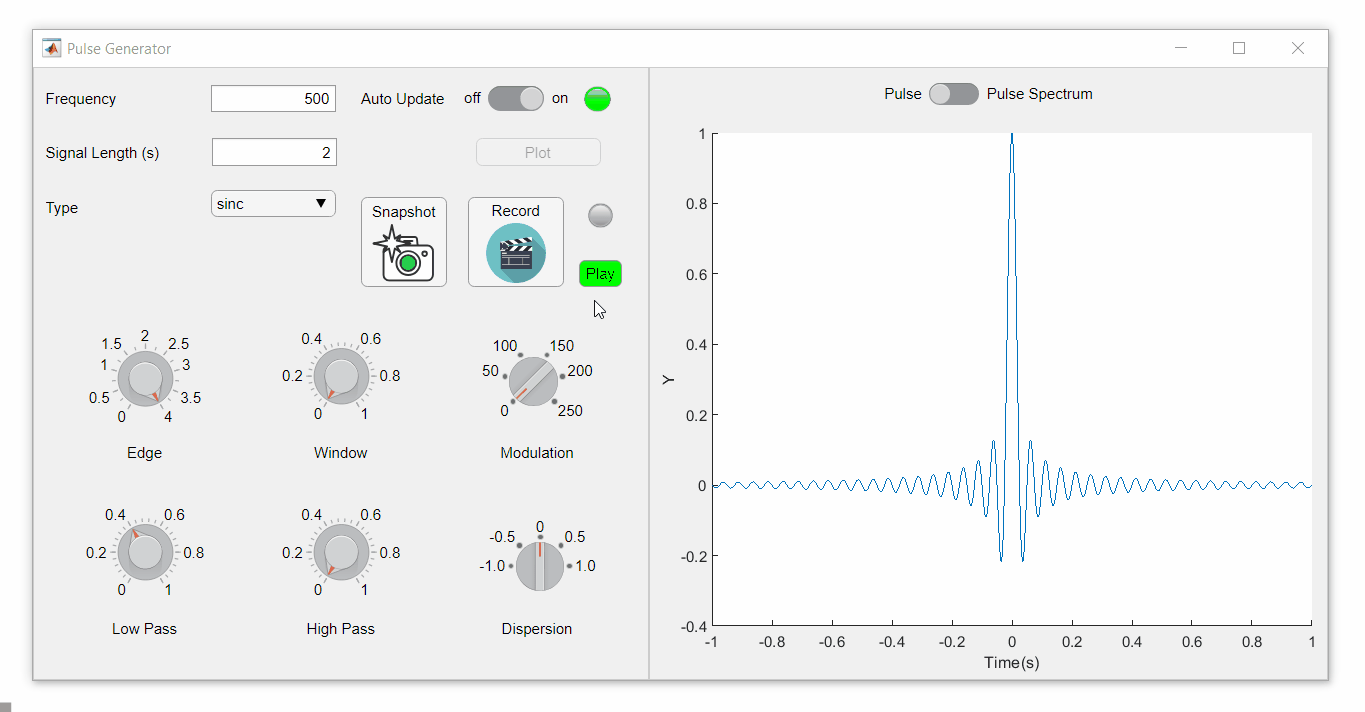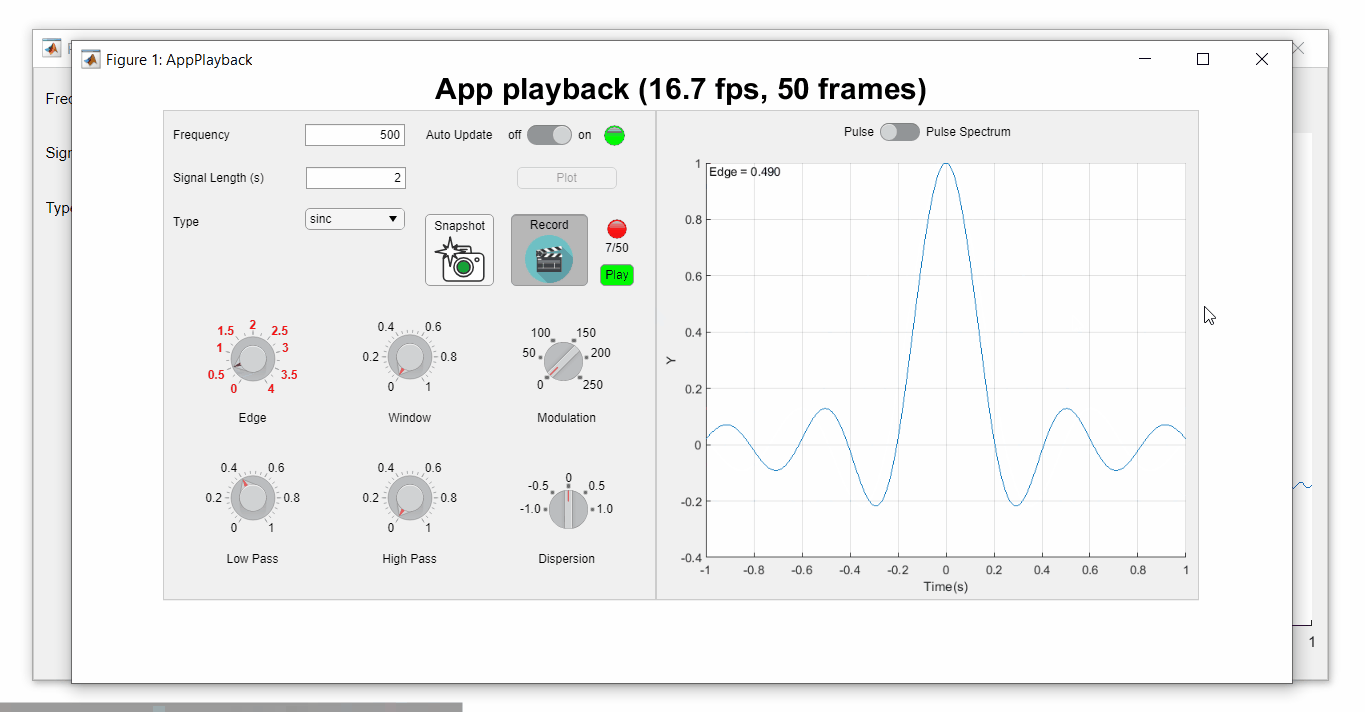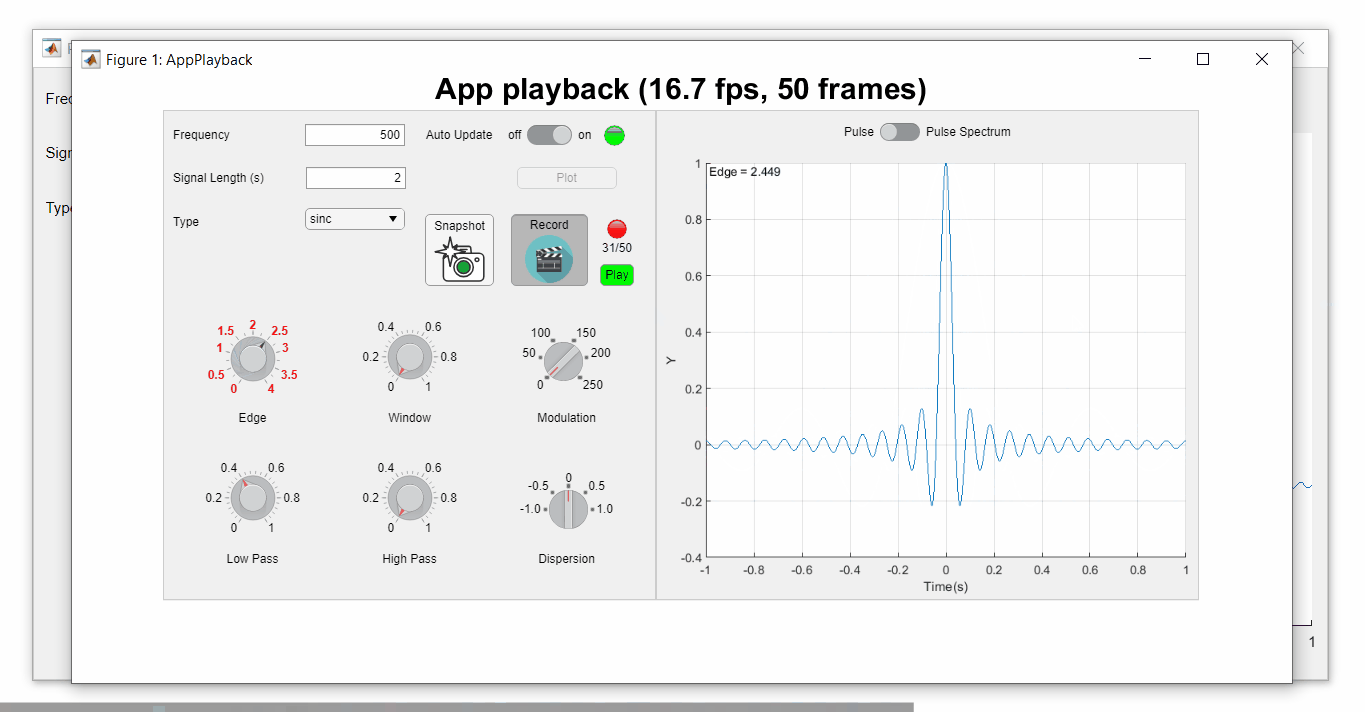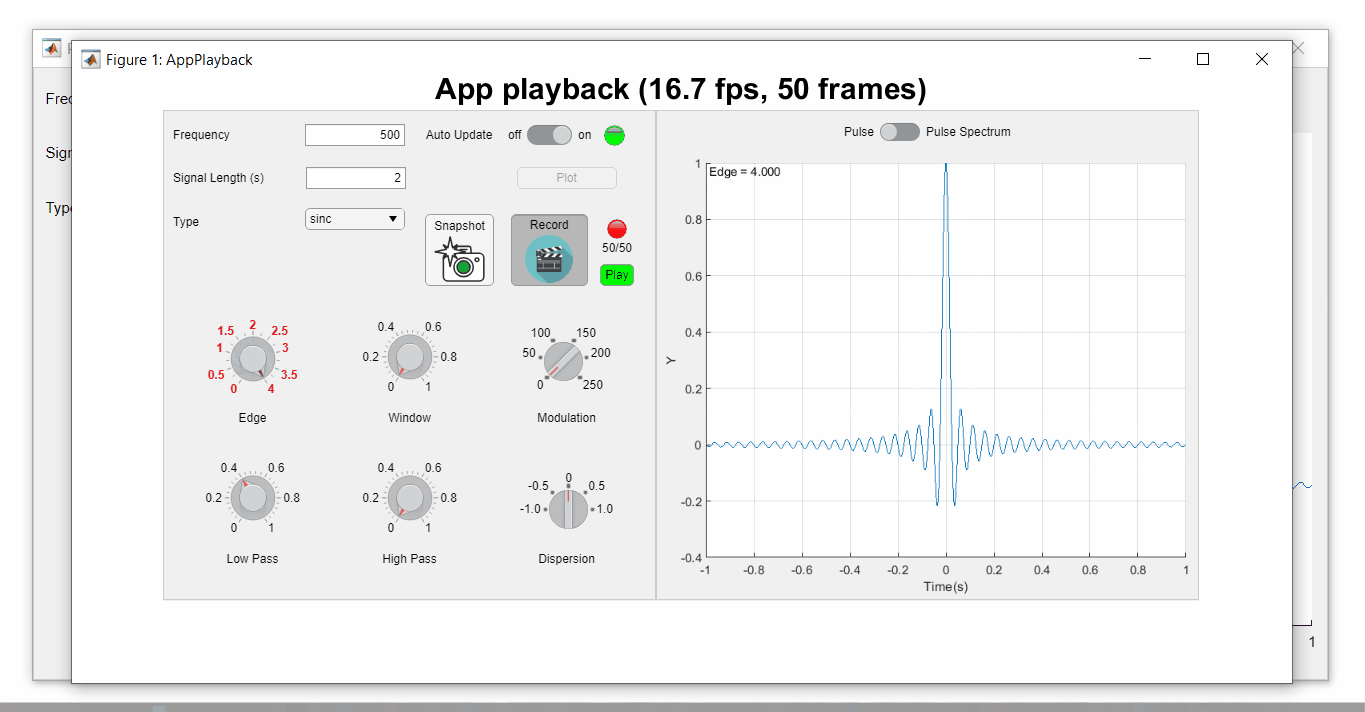
To demonstrate this, I adapted a copy of Matlab's built-in PulseGenerator.mlapp by adding
- a record button
- a record status lamp with frame counter
- a playback button
- a function that animates the effects of the Edge Knob
Recording process (The GIF is a lot faster than realtime and only shows part of the recording) (Open the image in a new window or see the attached Live Script for a clearer image).
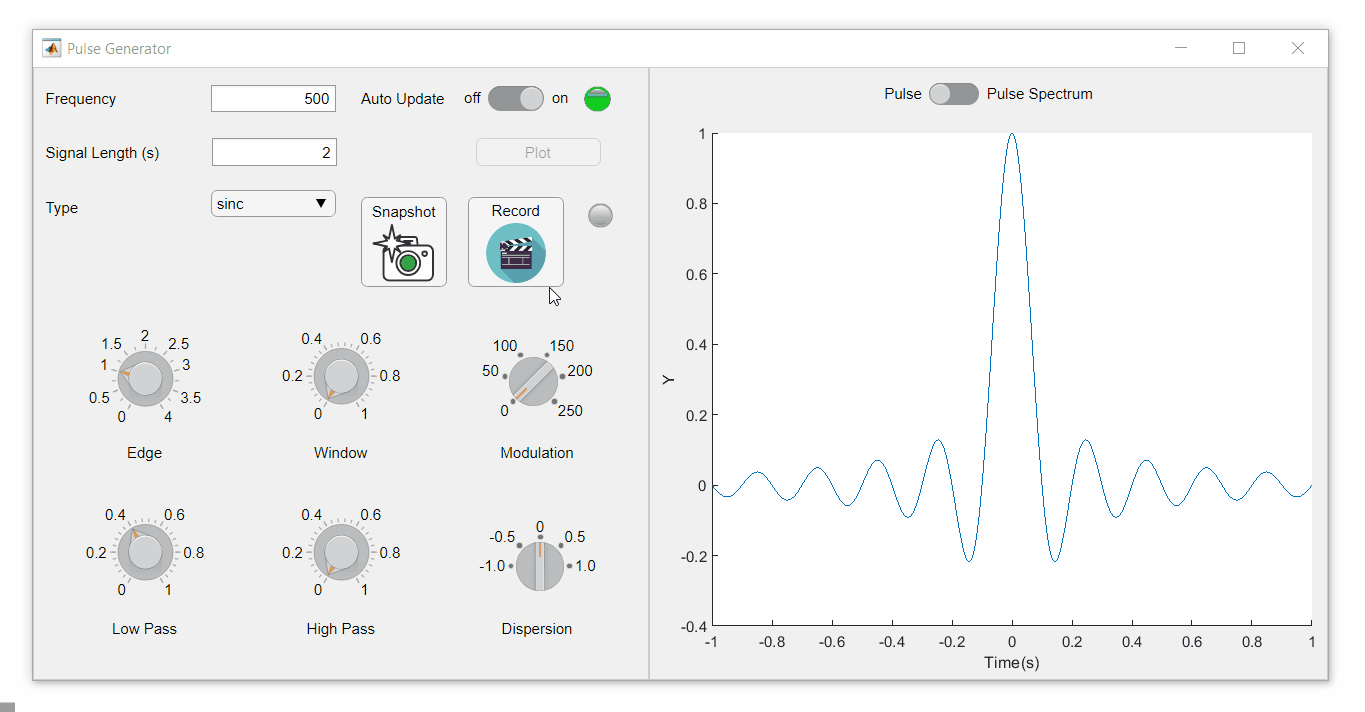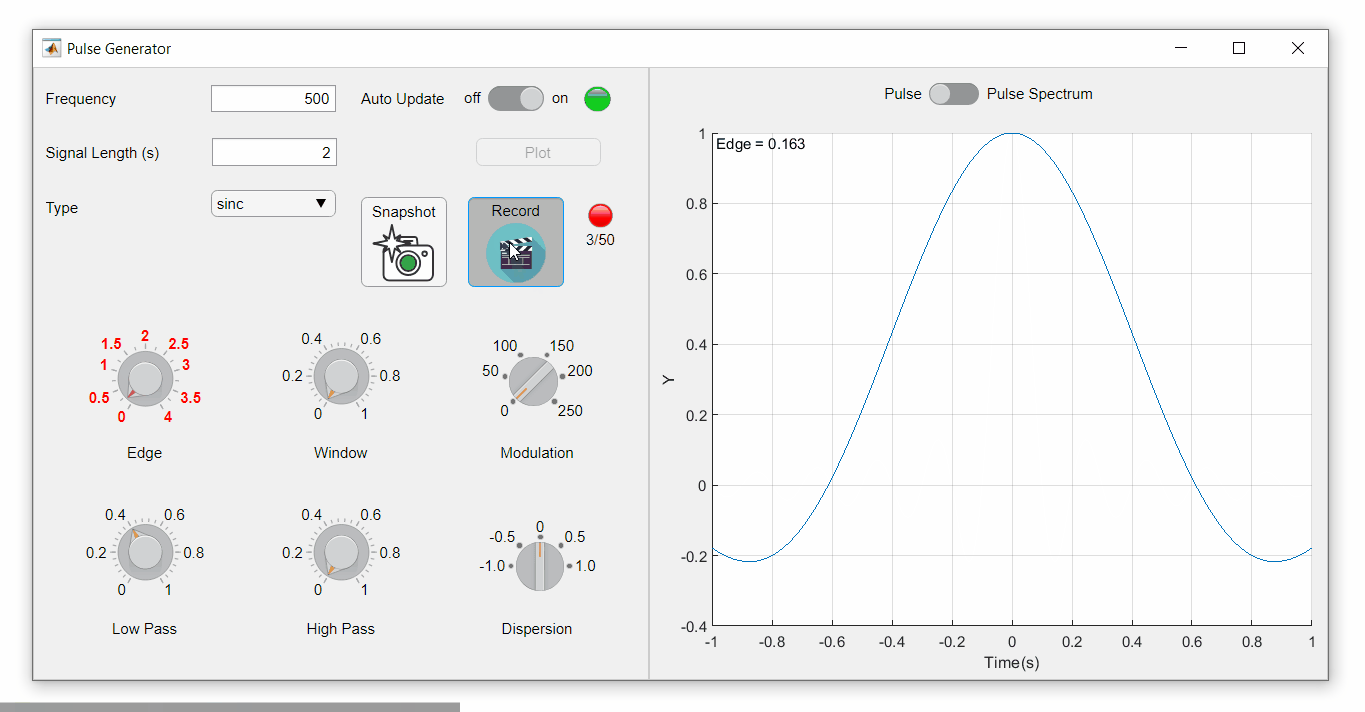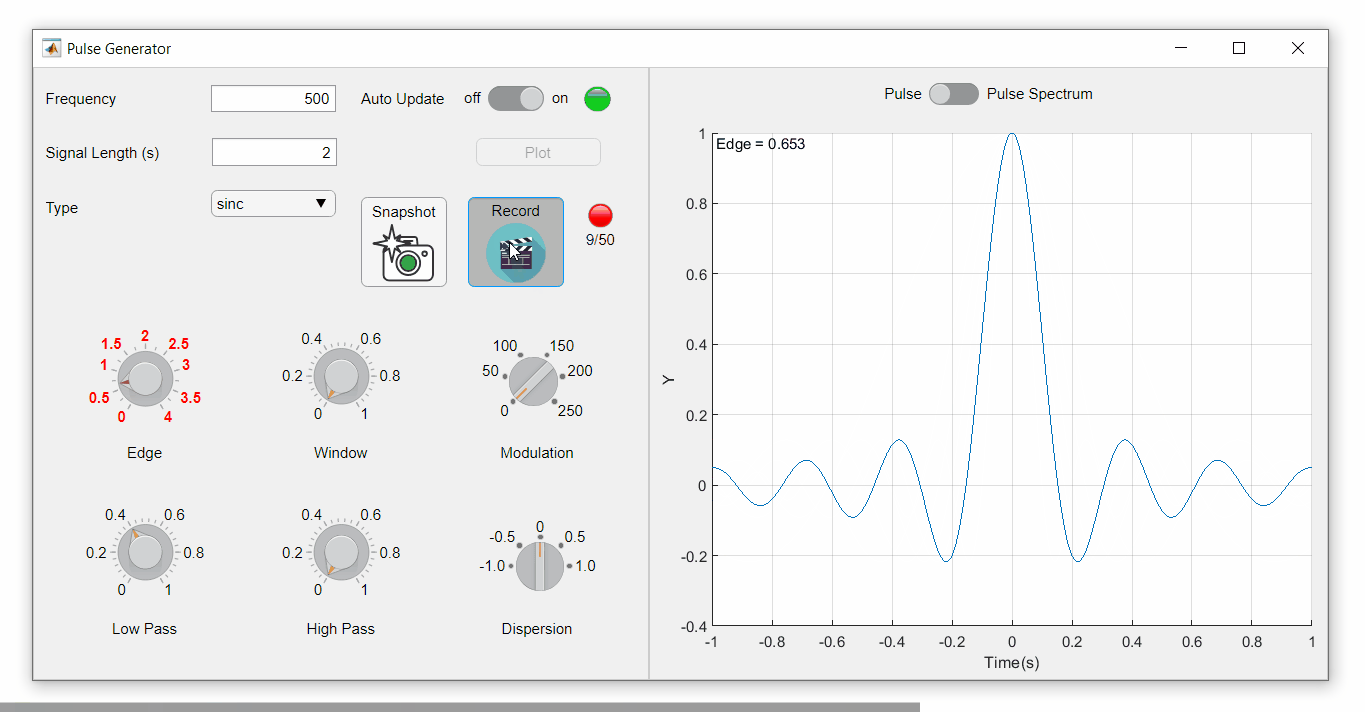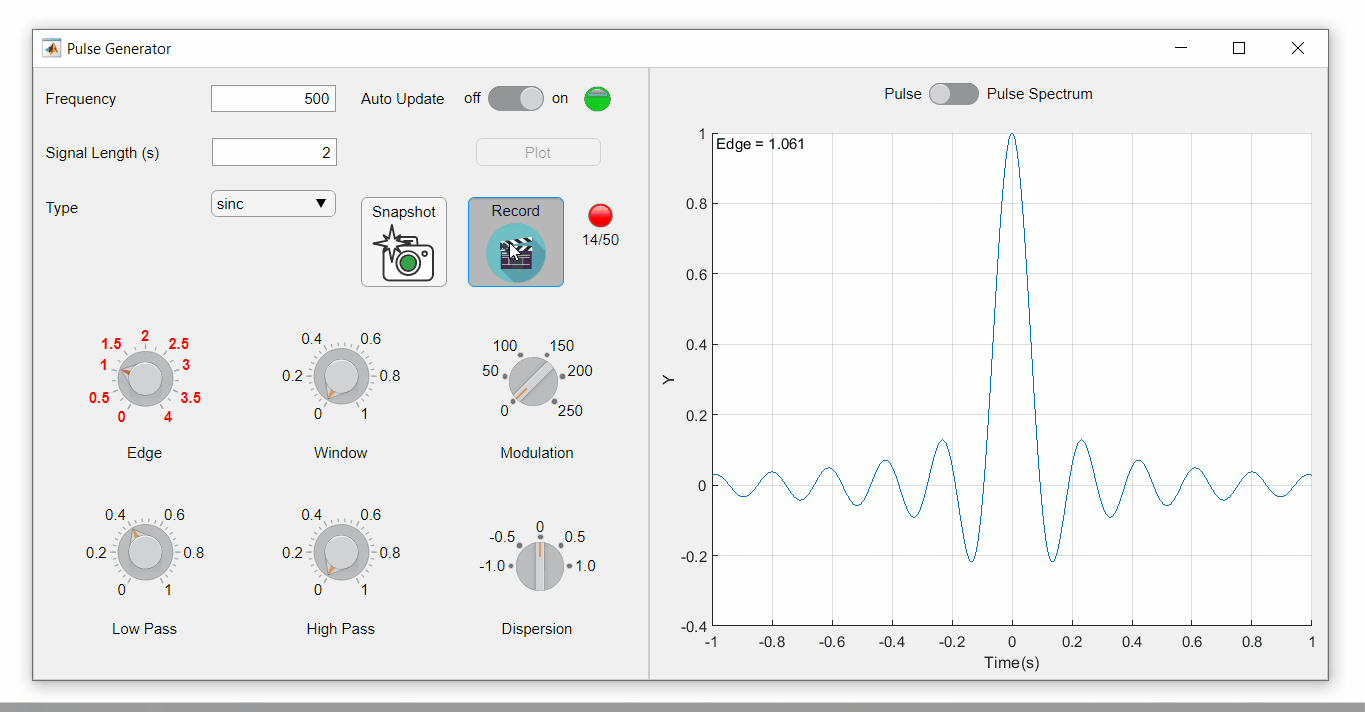
Playback process (Open the image in a new window or see the attached Live Script for a clearer image.)
Review: How to get the handle to an app figure
To use either of these functions outside of app designer, you'll need to access the App's figure handle. By default, the HandleVisibility property of uifigures is set to off preventing the use of gcf to retrieve the figure handle. Here are 4 ways to access the app's figure handle from outside of the app.
1. Store the app's handle when opening the app.
app = myApp; % Get the figure handle figureHandle = app.myAppUIFigure;
2. Search for the figure handle using the app's name, tag, or any other unique property value
allfigs = findall(0, 'Type', 'figure'); % handle to all existing figures figureHandle = findall(allfigs, 'Name', 'MyApp', 'Tag', 'MyUniqueTagName');
3. Change the HandleVisibility property to on or callback so that the figure handle is accessible by gcf anywhere or from within callback functions. This can be changed programmatically or from within the app designer component browser. Note, this is not recommended since any function that uses gcf such as axes(), clf(), etc can now access your app!.
4. If the app's figure handle is needed within a callback function external to the app, you could pass the app's figure handle in as an input variable or you could use gcbf() even if the HandleVisibility is off.
See a complete list of changes to the PulseGenerator app in the attached Live Script file to recreate the app.

Starting in r2020a , you can change the mouse pointer symbol in apps and uifigures.
The Pointer property of a figure defines the cursor’s default pointer symbol within the figure. You can also create your own pointer symbols (see part 3, below).
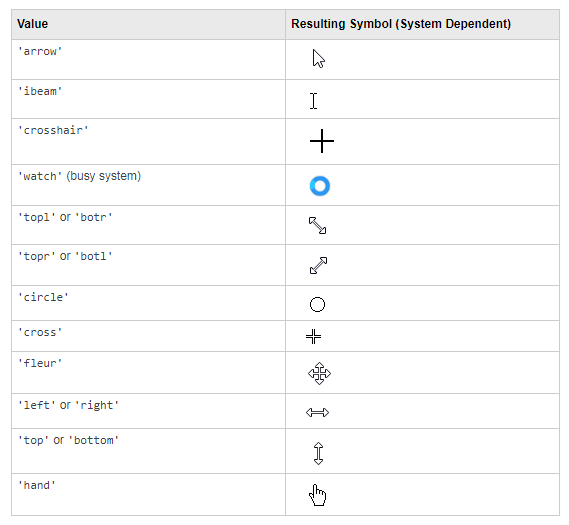
Part 1. How to define a default pointer symbol for a uifigure or app
For figures or uifigures, set the pointer property when you define the figure or change the pointer property using the figure handle.
% Set pointer when creating the figure
uifig = uifigure('Pointer', 'crosshair');
% Change pointer after creating the figure uifig.Pointer = 'crosshair';
For apps made in AppDesigner, you can either set the pointer from the Design View or you can set the pointer property of the app’s UIFigure from the startup function using the second syntax shown above.
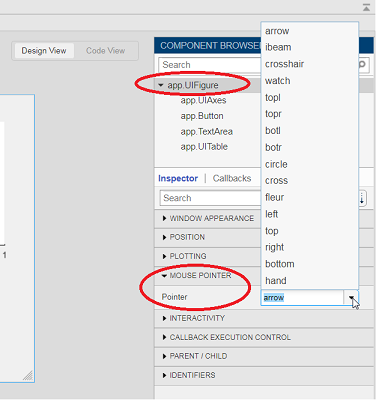
Part 2. How to change the pointer symbol dynamically
The pointer can be changed by setting specific conditions that trigger a change in the pointer symbol.
For example, the pointer can be temporarily changed to a busy-symbol when a button is pressed. This ButtonPushed callback function changes the pointer for 1 second.
function WaitasecondButtonPushed(app, event) % Change pointer for 1 second. set(app.UIFigure, 'Pointer','watch') pause(1) % Change back to default. set(app.UIFigure, 'Pointer','arrow') app.WaitasecondButton.Value = false; end
The pointer can be changed every time it enters or leaves a uiaxes or any plotted object within the uiaxes. This is controlled by a set of pointer management functions that can be set in the app’s startup function.
iptSetPointerBehavior(obj,pointerBehavior) allows you to define what happens when the pointer enters, leaves, or moves within an object. Currently, only axes and axes objects seem to be supported for UIFigures.
iptPointerManager(hFigure,'enable') enables the figure’s pointer manager and updates it to recognize the newly added pointer behaviors.
The snippet below can be placed in the app’s startup function to change the pointer to crosshairs when the pointer enters the outerposition of a uiaxes and then change it back to the default arrow when it leaves the uiaxes.
% Define pointer behavior when pointer enter axes pm.enterFcn = @(~,~) set(app.UIFigure, 'Pointer', 'crosshair'); pm.exitFcn = @(~,~) set(app.UIFigure, 'Pointer', 'arrow'); pm.traverseFcn = []; iptSetPointerBehavior(app.UIAxes, pm)
% Enable pointer manager for app iptPointerManager(app.UIFigure,'enable');
Any function can be triggered when entering/exiting an axes object which makes the pointer management tools quite powerful. This snippet below defines a custom function cursorPositionFeedback() that responds to the pointer entering/exiting a patch object plotted within the uiaxes. When the pointer enters the patch, the patch color is changed to red, the pointer is changed to double arrows, and text appears in the app’s text area. When the pointer exits, the patch color changes back to blue, the pointer changes back to crosshairs, and the text area is cleared.
% Plot patch on uiaxes
hold(app.UIAxes, 'on')
region1 = patch(app.UIAxes,[1.5 3.5 3.5 1.5],[0 0 5 5],'b','FaceAlpha',0.07,...
'LineWidth',2,'LineStyle','--','tag','region1');
% Define pointer behavior for patch pm.enterFcn = @(~,~) cursorPositionFeedback(app, region1, 'in'); pm.exitFcn = @(~,~) cursorPositionFeedback(app, region1, 'out'); pm.traverseFcn = []; iptSetPointerBehavior(region1, pm)
% Enable pointer manager for app iptPointerManager(app.UIFigure,'enable');
function cursorPositionFeedback(app, hobj, inout)
% When inout is 'in', change hobj facecolor to red and update textbox.
% When inout is 'out' change hobj facecolor to blue, and clear textbox.
% Check tag property of hobj to identify the object.
switch lower(inout)
case 'in'
facecolor = 'r';
txt = 'Inside region 1';
pointer = 'fleur';
case 'out'
facecolor = 'b';
txt = '';
pointer = 'crosshair';
end
hobj.FaceColor = facecolor;
app.TextArea.Value = txt;
set(app.UIFigure, 'Pointer', pointer)
end
The app showing the demo below is attached.
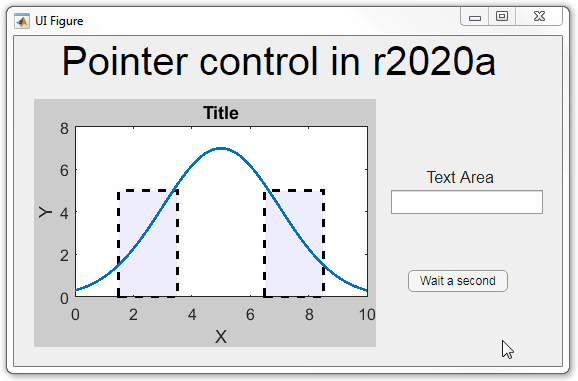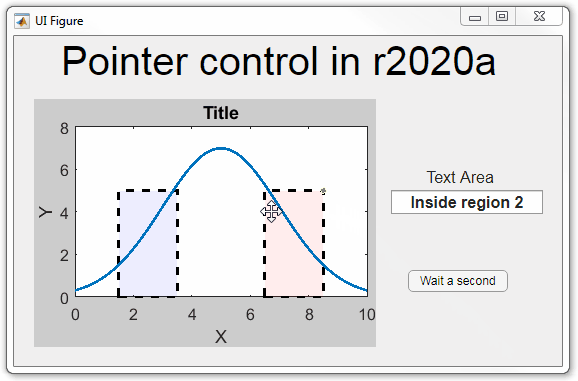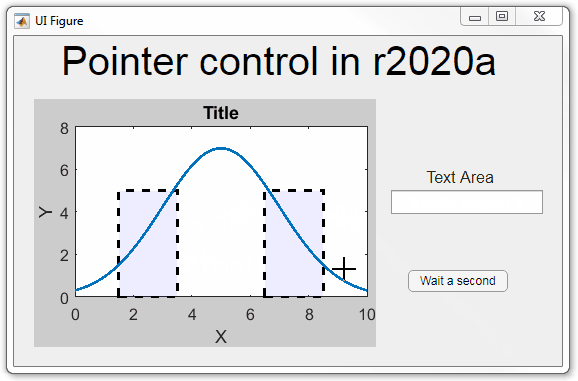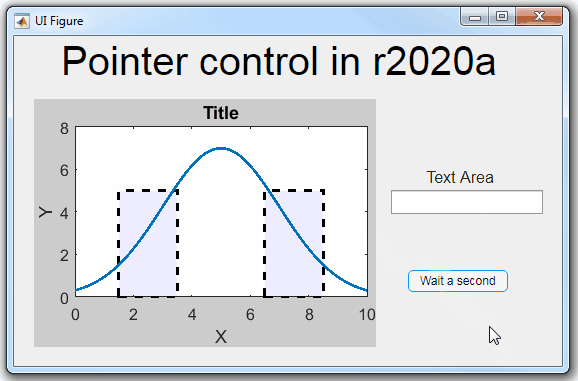
Part 3. Create your own custom pointer symbol
- Set the figure’s pointer property to ‘custom’.
- Set the figure’s PointerShapeCData property to the custom pointer matrix. A custom pointer is defined by a 16x16 or 32x32 matrix where NaN values are transparent, 1=black, and 2=white.
- Set the figure’s PointerShapeHotSpot to [m,n] where m and n are the coordinates that define the tip or "hotspot" of the matrix.
This demo uses the attached mat file to create a black hand pointer symbol.
iconData = load('blackHandPointer.mat');
uifig = uifigure();
uifig.Pointer = 'custom';
uifig.PointerShapeCData = iconData.blackHandIcon;
uifig.PointerShapeHotSpot = iconData.hotspot;
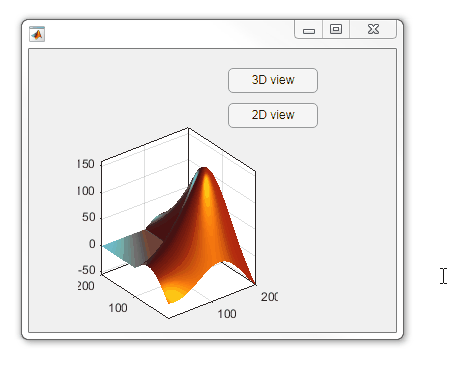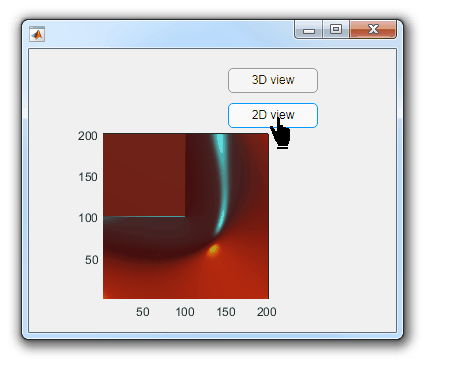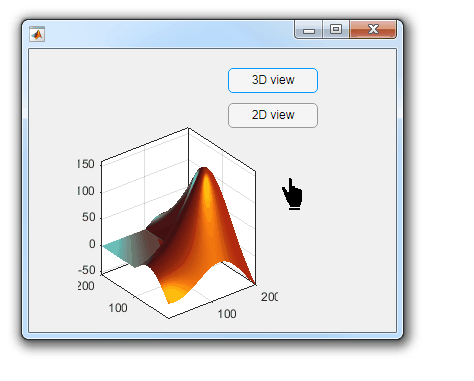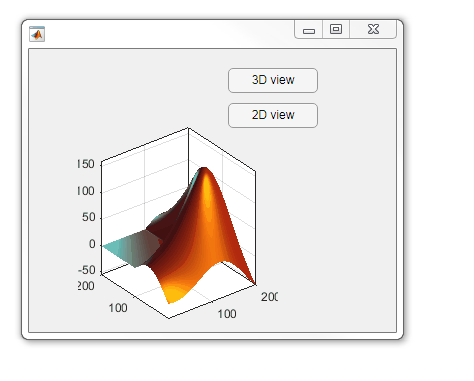
Also see Jiro's pointereditor() function on the file exchange which allows you to draw your own pointer.